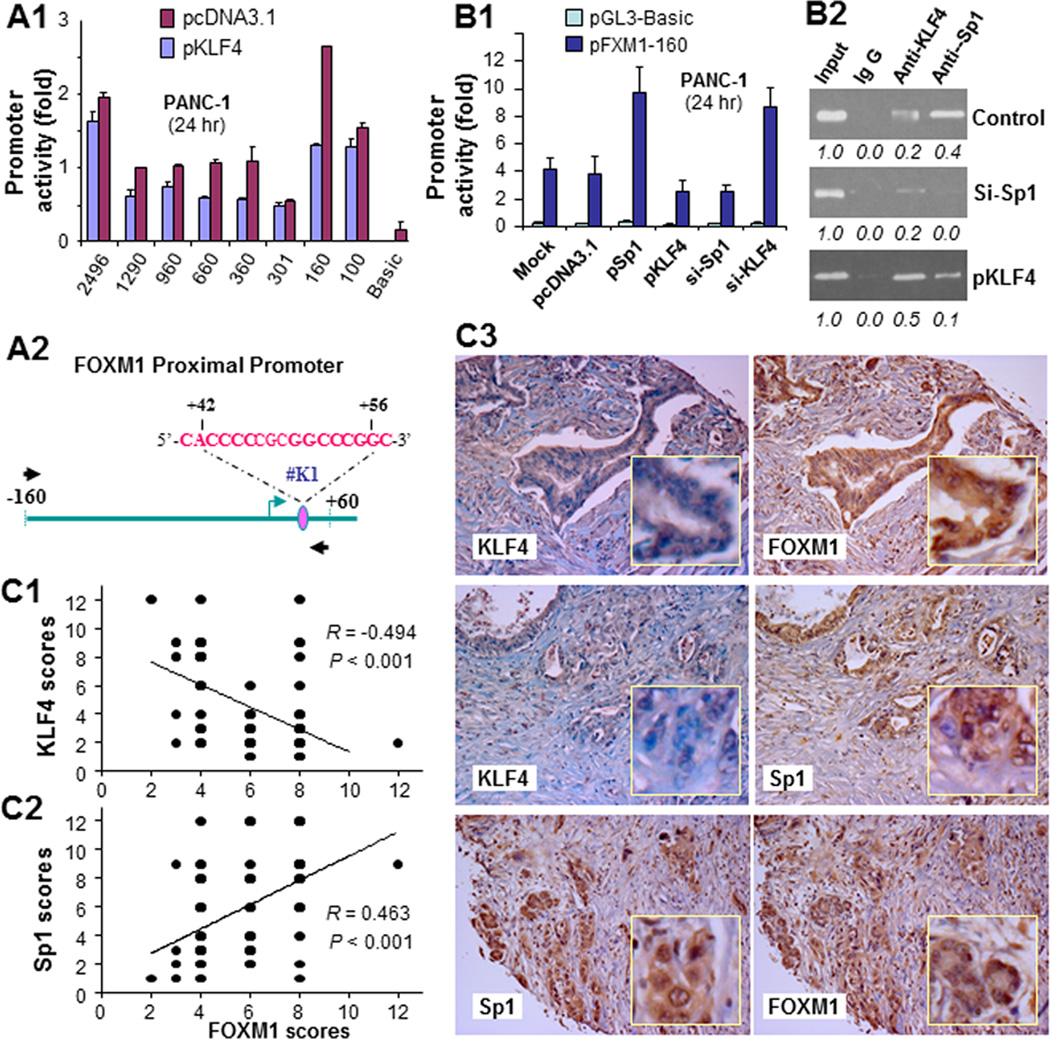
Figure 5.
Regulation of FOXM1 promoter activity by KLF4 and Sp1. A, the FOXM1 promoter reporters were transfected into PANC-1 cells in triplicate with or without a KLF4 expression vector; pcDNA3.1 was used as a control. The relative FOXM1 promoter activity was measured 24 hours after transfection, and the activity in the treated groups was expressed as the fold of that in their respective control groups (image 1). A schematic of the structure of the minimal FOXM1 promoter reporter construct pFXM1-160 with a putative Sp1/KLF4-binding site is also shown (image 2). B, the pFXM1-160 reporter was transfected into PANC-1 cells in triplicate with or without a KLF4 expression vector (pKLF4), Sp1 expression vector (pSp1), Sp1 siRNA (si-Sp1), or KLF4 siRNA (si-KLF4); nontargeting siRNA (mock) and pcDNA3.1 were used as controls. The relative FOXM1 promoter activity was measured 24 hours after transfection (image 1). The in vivo binding of Sp1 and KLF4 to their putative binding sites and altered binding of them upon increased or decreased expression of KLF4 or Sp1 in PANC-1 cells was examined using a ChIP assay (image 2). C, FOXM1, KLF4, and Sp1 expression in human pancreatic tumors and normal pancreatic tissue was measured using standard immunohistochemical procedures with specific anti-FOXM1, -KLF4, and -Sp1 antibodies. FOXM1 expression correlated inversely with KLF4 expression (image 1) but directly with Sp1 expression (image 2). Representative photos of the expression of FOXM1, KLF4, and Sp1 in pancreatic tumors are shown (image 3). Note: some of the dots on the graphs represent more than one specimen (overlapped scores).