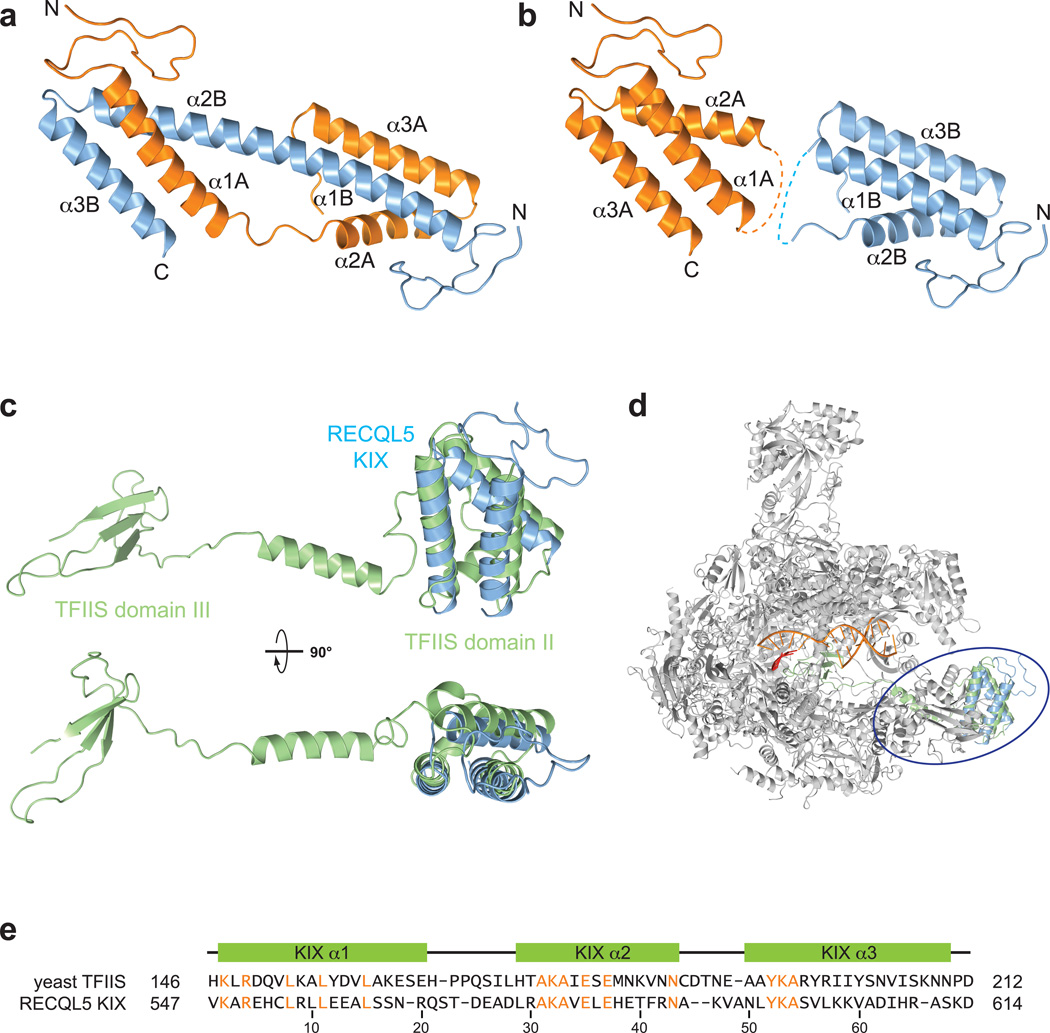
Figure 2. The RECQL5 KIX domain resembles domain II of TFIIS.
(a) Crystal structure of the domain–swapped RECQL5 KIX dimer. Alpha–helical segments are labeled for the two chains. (b) KIX domain monomers derived from the dimeric crystal structure. Dashed lines indicate loops connecting helices α1 and α2 in KIX domain monomers. (c) Superposition of TFIIS (green, PDB code 3PO3) and the RECQL5 KIX domain shown in two orthogonal orientations. (d) Superposition of the RECQL5 KIX domain (blue) onto domain II of TFIIS (green) in complex with Pol II (grey, PDB code 3PO3). (e) Structure–based sequence alignment of domain II of yeast TFIIS and the human RECQL5 KIX domain. Identical residues are highlighted in orange. Secondary structure elements are shown relative to the RECQL5 sequence.