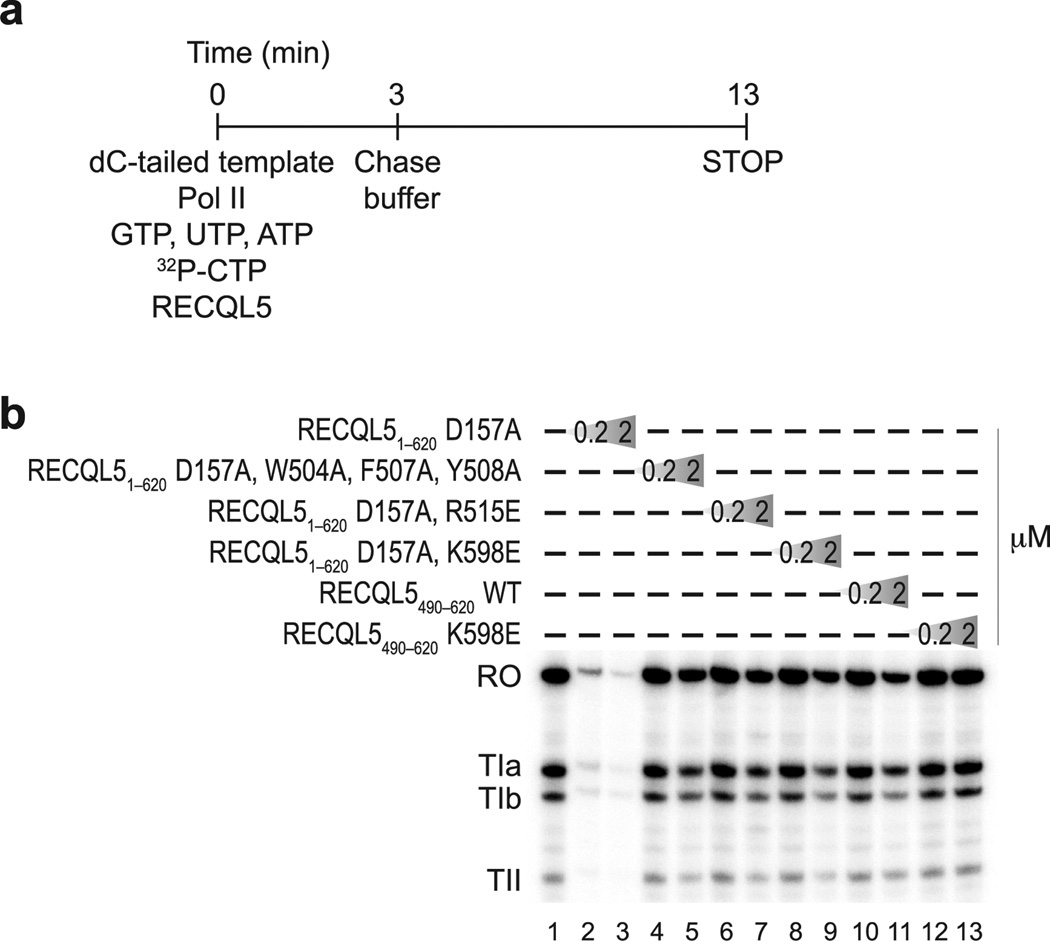
Figure 5. Both RECQL5 helicase and IRI domains are required for repression of transcription.
(a) Schematic overview of the in vitro transcription assay. The dC–tailed histone H3.3 intron DNA was used as template and transcribed by purified Pol II (0.8 pmol) in the presence of recombinant wild–type and mutant RECQL5 proteins at two different concentrations (0.2 µM and 2 µM, corresponding to a 5–fold and 50–fold molar excess over Pol II, respectively). (b) Transcription assay performed as outlined in (a) in the presence of recombinant RECQL5 fragments and their mutants, as indicated. Transcripts were resolved by electrophoresis on a denaturing polyacrylamide gel and visualized by phosphorimaging. The transcription template contains three stall sites, giving rise to stalled transcripts TIa, TIb, and TII in addition to the run–off transcript (RO).