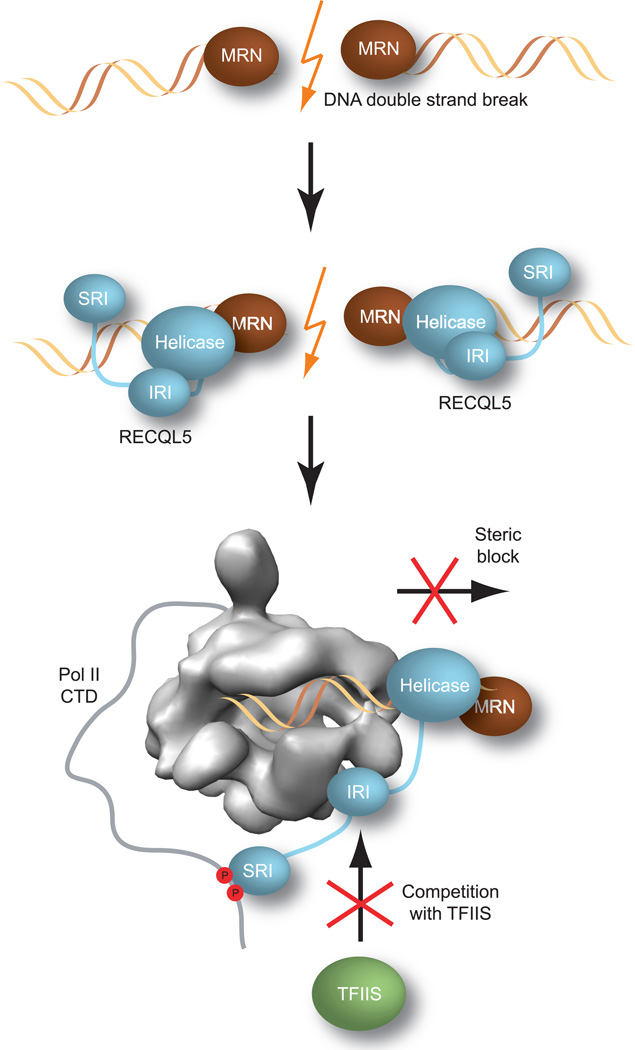
Figure 7. Dual mechanism of RECQL5–mediated transcriptional repression in DNA repair.
RECQL5 is recruited by the MRN complex to DNA double–strand breaks, where it inhibits transcription through two concerted mechanisms. The DNA–bound helicase domain of RECQL5 acts as a steric block to prevent Pol II from proceeding towards the site of DNA damage. Concurrently, the IRI domain of RECQL5 inhibits binding of TFIIS to Pol II, thereby preventing repeated cycles of TFIIS–mediated backtracking and elongation at the stall site.