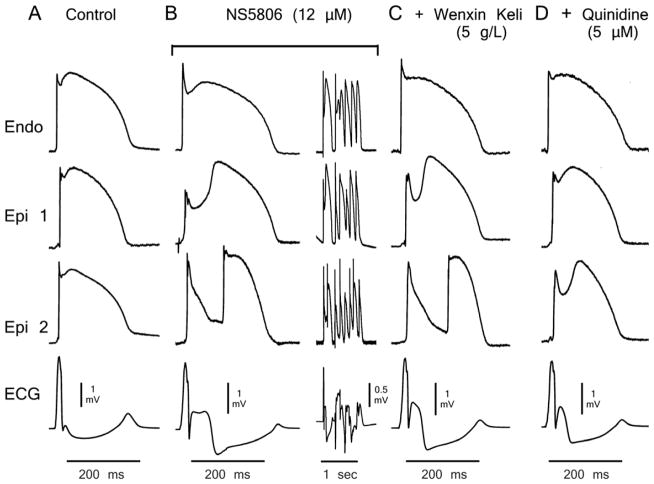
Figure 2.
Wenxin Keli (5g/L) and quinidine (5 μM) suppression of NS5806-induced Brugada syndrome phenotype. Shown are transmembrane action potentials (APs) simultaneously recorded from two sites on the epicardial (Epi) surface and one site on the endocardial (Endo) surface of a coronary-perfused right ventricular wedge preparation. The bottom trace is the pseudo-electrocardiogram (ECG) recorded across the bath. A: Control. B: The transient outward potassium channel current agonist NS5806 (12 μM) accentuates the Epi AP notch and electrocardiographic J wave, leading to loss of the AP dome at Epi1 but not Epi2. Heterogeneous loss of the dome leads to the development of a closely–coupled phase 2 reentrant extrasystole which precipitates a polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. C: Wenxin Keli (5g/L) suppressed ventricular fibrillation but did not prevent phase 2 reentry. D: The combination of Wenxin Keli (5g/L) and quinidine restored homogeneity and aborted all arrhythmic activity. Basic cycle length=2000 ms.