Figure 7.
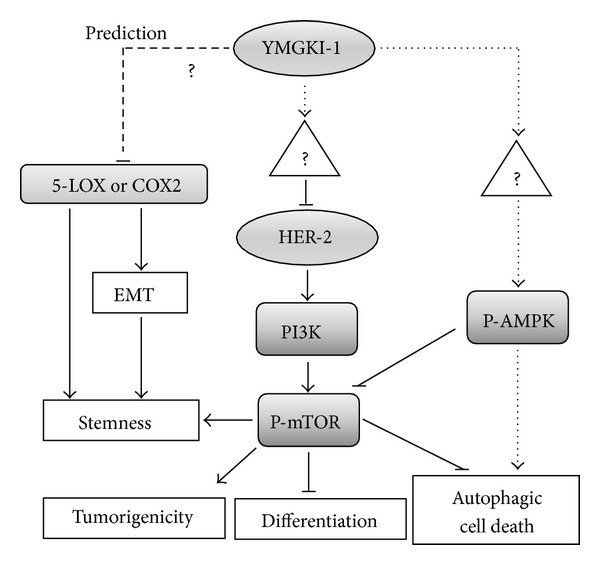
Schematic of the possible signaling pathways regulated by YMGKI-1, through which to inhibit the EMT, stemness properties, and tumorigenicity of head and neck cancer initiating cells (HN-CICs). The HER2/PI3K/MAPK/mTOR signaling pathway plays an important role in self-renewal, survival, and malignancy of CICs. YMGKI-1 would directly or indirectly inhibit the HER2/PI3K/MAPK/mTOR pathway. Further, an YMGKI-1 analogue is predicted to be a potential inhibitor of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) which are related to epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) [7]. YMGKI-1 might also prevent cells from undergoing EMT to gain stem cell properties via inhibiting COX-2 or 5-LOX. (—) refers to known pathway; (- - -) refers to unknown relationship; (……) refers to prediction.
