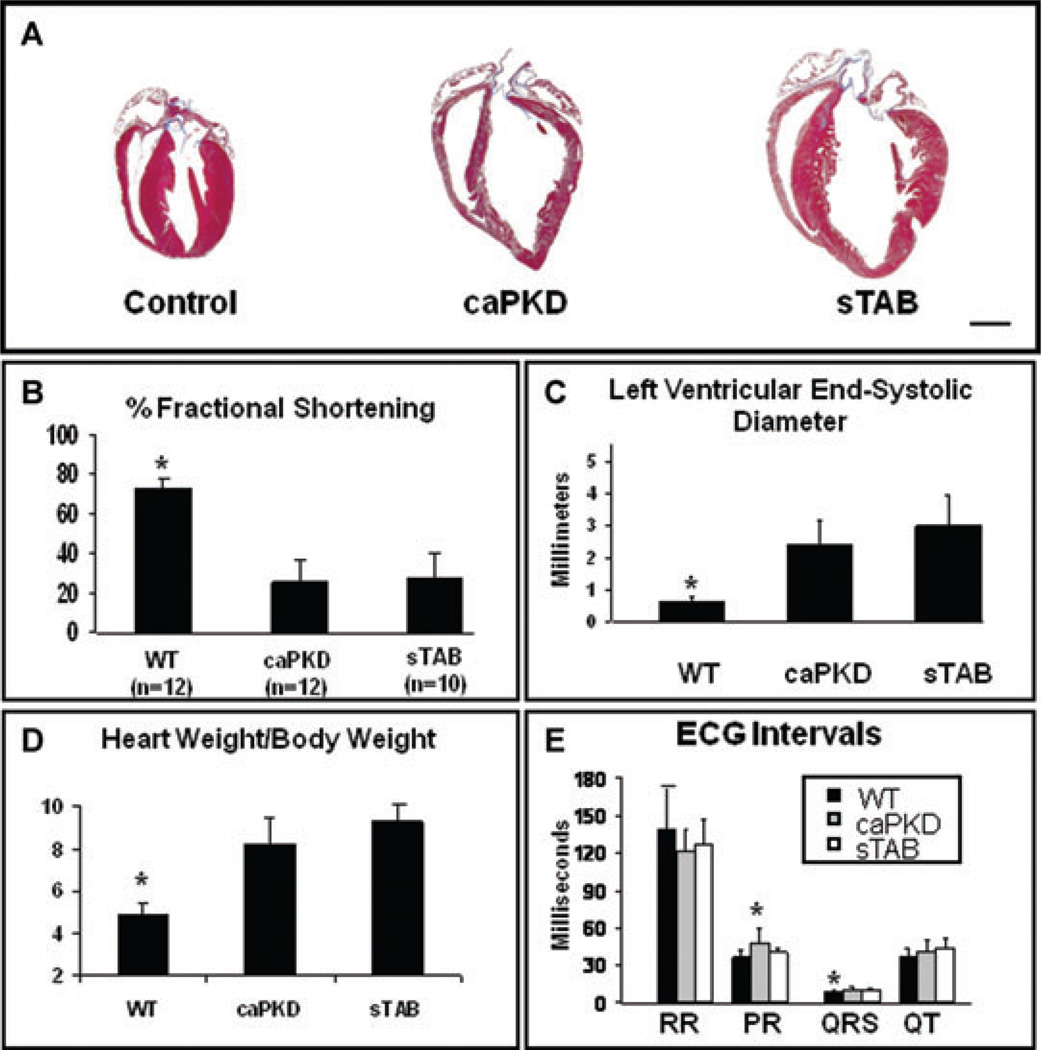
Figure 1.
(A) Representative histological heart sections from WT, caPKD, and sTAB-operated animals showed similar degrees of cardiac enlargement and dilation in sTAB-operated and caPKD transgenic animals. Echocardiographic assessment based on M-mode images showed significantly depressed left ventricular function in both the sTAB and caPKD mice (B) and comparable increases in the left ventricular systolic diameters (C). Assessment of heart mass revealed comparable increases in heart weight to body weight ratio in sTAB and caPKD mice (D). PR interval was slightly prolonged in caPKD mice as compared with WT and sTAB animals, and QRS interval was shorter in WT animals as compared with sTAB and caPKD animals. There were no significant differences between the groups in various other electrocardiographic intervals, under resting sedated conditions (E). Vertical bars represent S.E.M. * denotes P < 0.05. Bar of measure equals 2 mm.