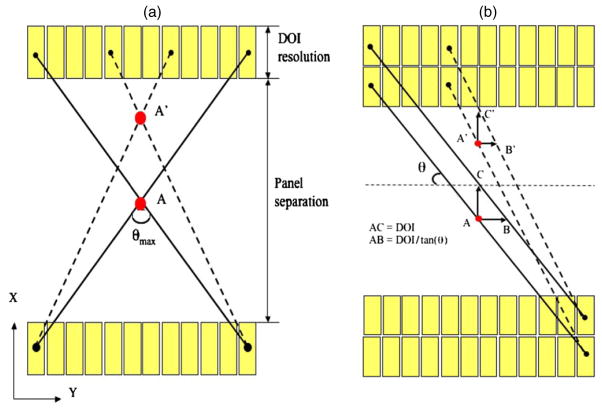
Figure 13.
(a) Illustration of the limited angle tomography effect. The dual-panel geometry only covers a certain limited range of projection angles (θmax less than 180°) and the incomplete angular sampling would cause resolution degradation or artifacts along the X direction (orthogonal to panels). (b) Illustration of the DOI blurring effect (also known as parallax error) and how it affects both the in-plane and orthogonal-plane resolutions. Only two layers of detectors are shown. For an adjacent parallel LOR pair, the effective blurring (i.e. parallax error) is AB (A′B′) along the Y direction (which affects the in-plane resolution) and AC (A′C′) along the X direction (which affects the orthogonal-plane resolution).