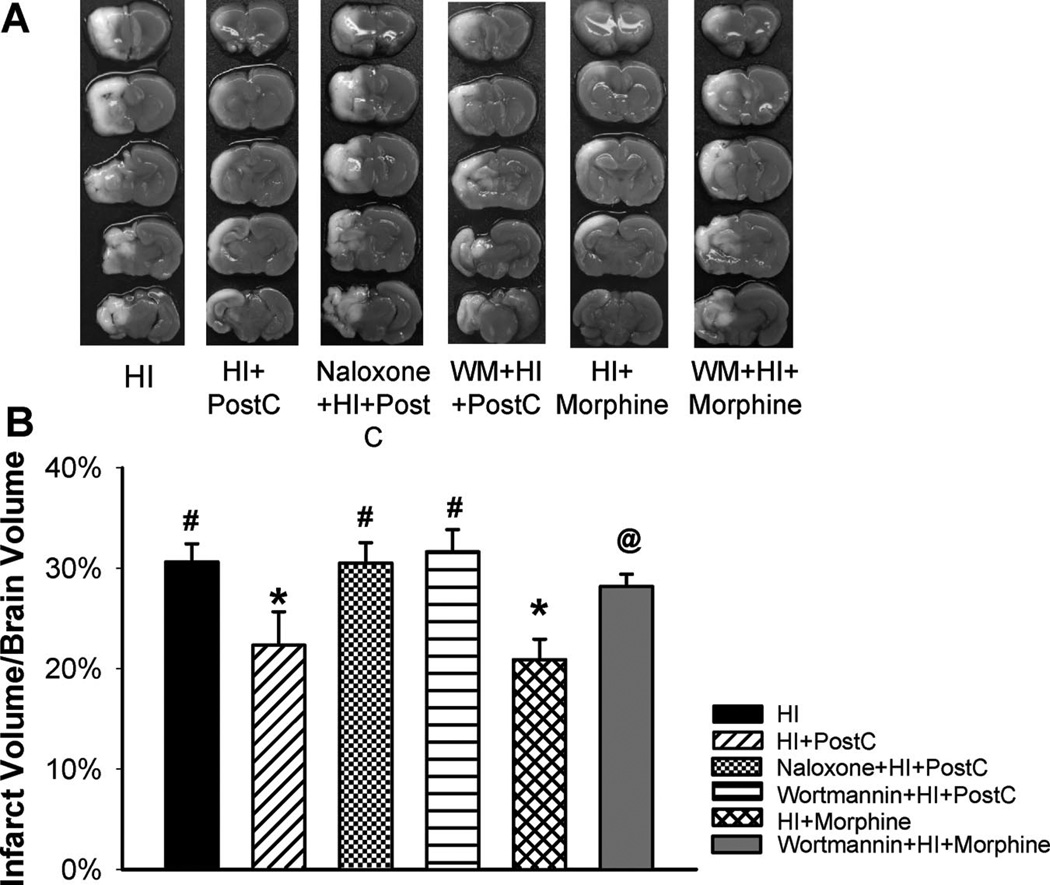
Figure 1.
Representative pictures of 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride monohydrate-stained coronal brain slices from each group (A) and quantitative analysis of infarct volume (B) in the HI group and groups treated with limb ischemic postconditoning (HI+PostC), naloxone+postconditioning (naloxone+HI+PostC), wortmannin+postconditioning (WM+HI+PostC), morphine (HI+morphine), and wortmannin+morphine (WM+HI+morphine) at 48 hours after HI; n=8 to 10 in each group. Limb ischemic postconditioning and morphine treatment resulted in significant reduction in infarct volume, respectively. Pretreatment with naloxone or wortmannin abolished the reduction in infarct volume induced by postconditioning. Wortmannin also blocked morphineinduced infarct sparing effect. Values are the mean±SEM; *P<0.05 versus HI group; #P<0.05 versus postconditioning-treated group; @P<0.05 versus morphine-treated group.