Figure 1. Experimental design for rodent study.
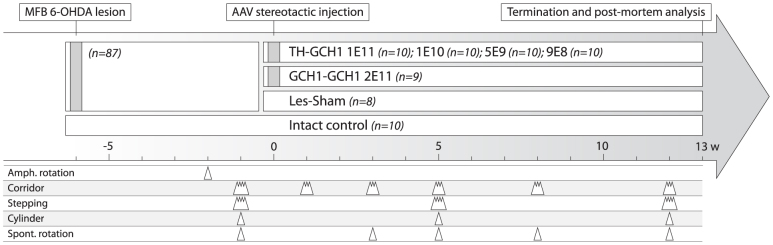
Fifty-seven rats with complete lesions that fulfilled the criteria of > 6 net ipsiversive rotations over 90 min upon challenge with D-amphetamine (2.5 mg/kg) were included in the study. The animals were behaviorally characterized using corridor, stepping and cylinder tests and allocated to one of 6 groups based on their performance either to receive different doses of the TH-GCH1 vector (TH-GCH1:1E11, 1E10, 5E9 and 9E8 gc) or followed as one of two control groups (GCH1-GCH1:2E11 gc or Les-Sham). In addition, an intact control group (n = 10) was included in the study. Animals were followed over a 12-week period with behavioral tests to assess motor function as indicated in the time line. Thirteen weeks after AAV treatment, animals from each experimental group were sacrificed for either histology and stereology (n = 6) or biochemical analysis (n = 4, data not shown).
