Fig. 1. Schematic representation of KIR haplotypes A and B.
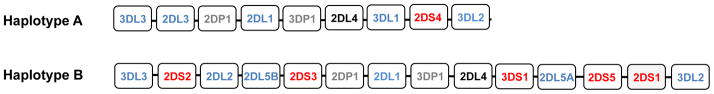
Genes encoding activating KIRs are shown in red, inhibitory KIRs are shown in blue and pseudogenes in grey. KIR2DL4, which has features of both an activating and an inhibitory receptor is shown in black.
