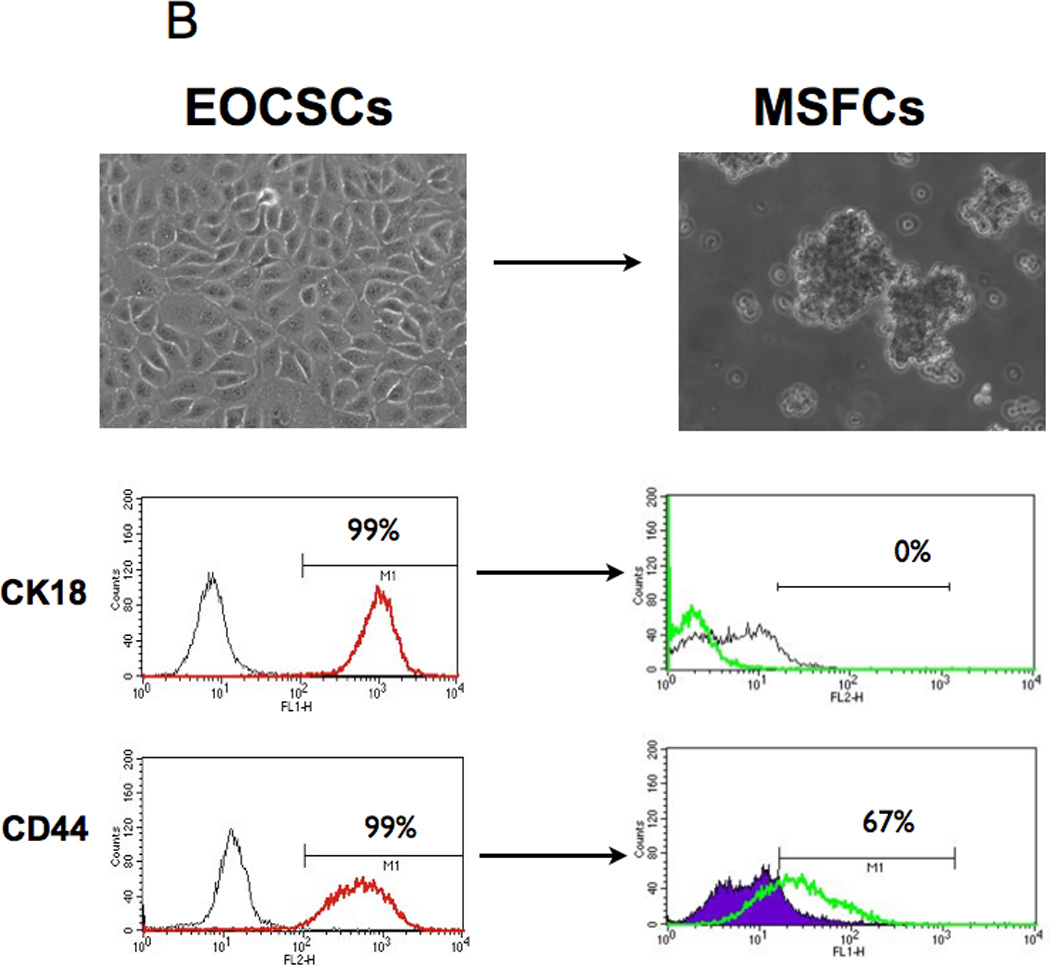
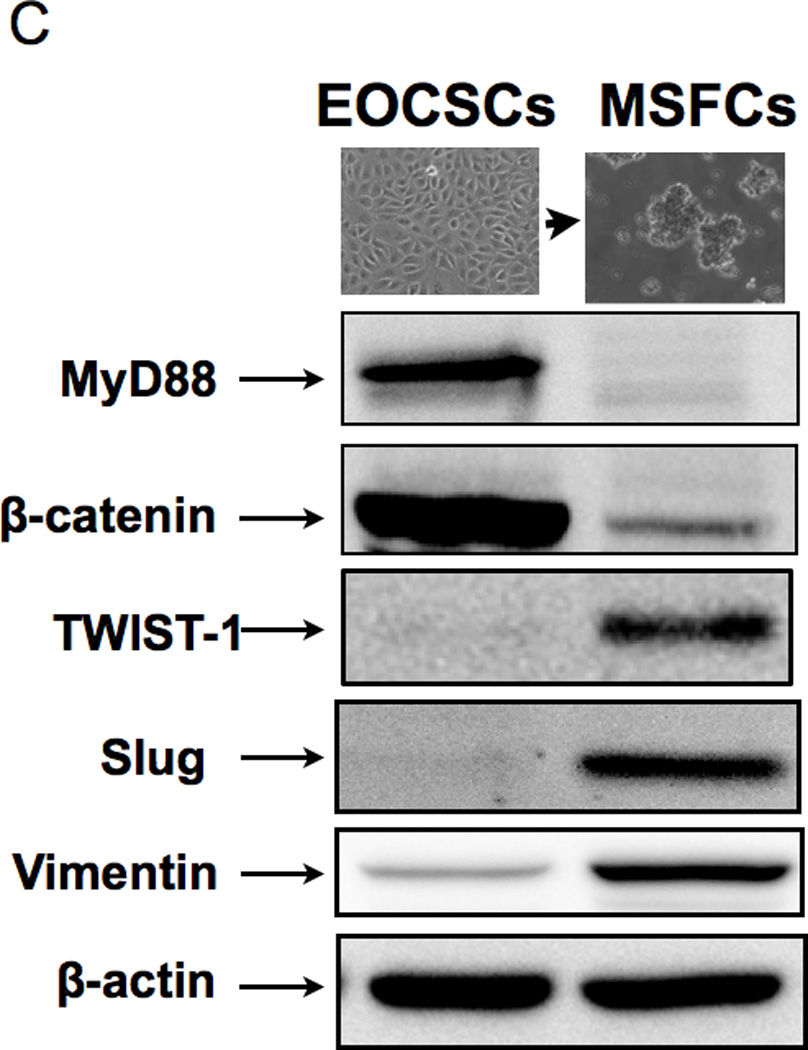
Figure 1. In vitro differentiation of CD44+/MyD88+ EOC stem cells into mesenchymal like spheroid-forming cells (MSFCs).
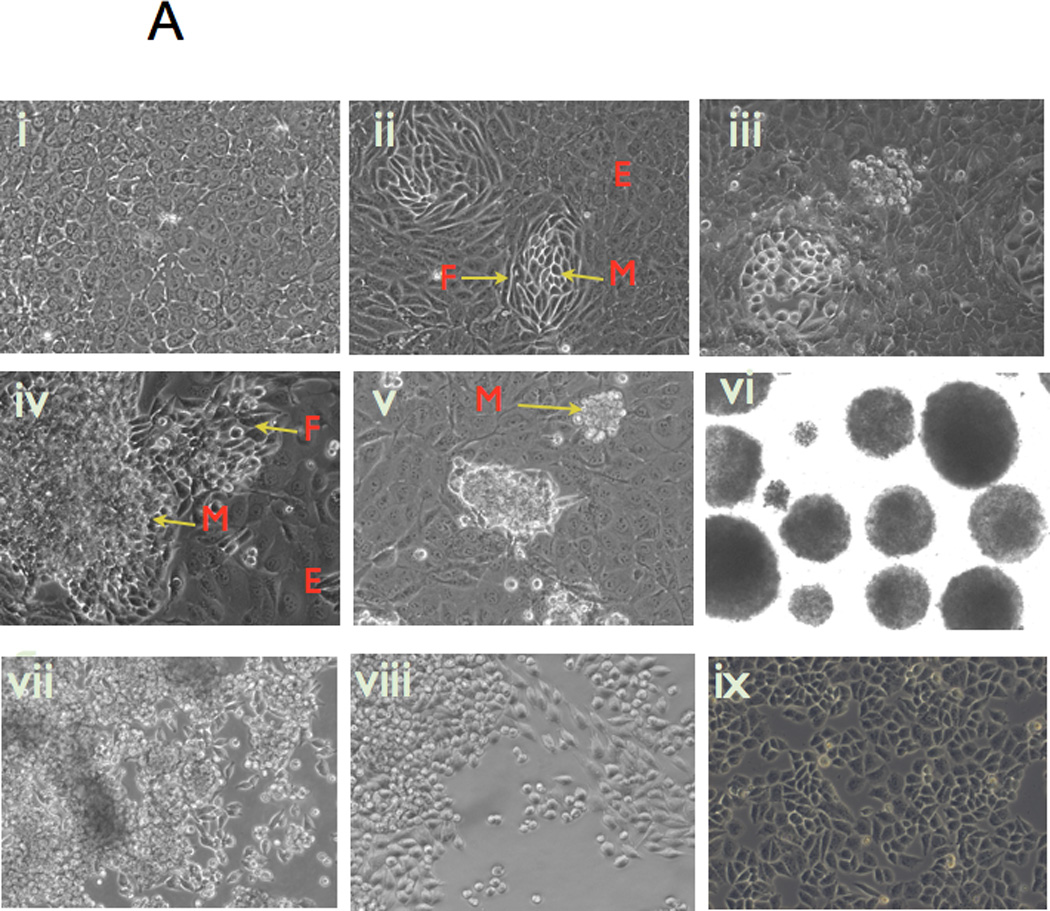
A) Over-confluent cultures of CD44+/MyD88+ EOC stem cells (i) form foci consisting of cells with fibroblast-like characteristics (ii-iv); these transformed cells eventually lose attachment and form mesenchymal compact spheroids (v-vi); spheroids can re-attach and re-form an epithelial monolayer when transferred to tissue culture plates (vii-ix);
(B-C Upon spheroid formation, CD44+/MyD88+ EOC stem cells have lower levels of the epithelial marker Ck18 and the cancer stem cell markers, CD44 and B-catenin; but gain mesenchymal markers TWIST-1, Slug, and Vimentin. E, epithelial; F, fibroblast-like; M, mesenchymal-like; EOCSC - CD44+/MyD88+ EOC stem cells; MSFC - mesenchymal spheroids forming cells. Figures are representative of three clones done in independent experiments. Every experiment was repeated at least three times.
