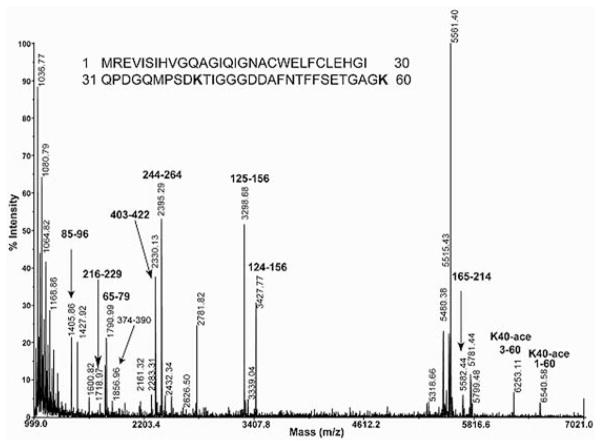
Figure 1. MS analysis of acetylation of lysine on T. gondii tubulin.
Trypsin specifically cleaves peptide bonds after lysine and arginine residues. The resulting peptides are labelled by their sequence location (e.g. 85–96, 216–229 etc.). K40-ace 3–60 and K40-ace 1–60 are peptides containing acetylated Lys40. Acetylation on Lys40 modifies the lysine residue making it unrecognizable by trypsin, resulting in a blocked cleavage site; thus tryptic peptides with one extra missed cleavage (1–60) and (3–60) are observed in the mass spectrum of a trypsin digestion of T. gondii α-tubulin. Additionally, the mass of these two peptides is +42 Da larger than their predicted masses of 6498.29 and 6210.91 respectively, confirming the presence of acetylation. Reprinted, with permission, from Hui Xiao, Kamal El Bissati, Pascal Verdier-Pinard, Berta Burd, Hongshan Zhang, Kami Kim, Andras Fiser, Ruth Hogue Angeletti and Louis M. Weiss (2010), Post-translational modifications to Toxoplasma gondii α- and β-tubulins include novel C-terminal methylation, Journal of Proteome Research, 9(1), pp. 359–372, Copyright (2010) American Chemical Society.