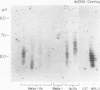
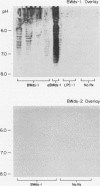
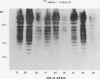
Abstract
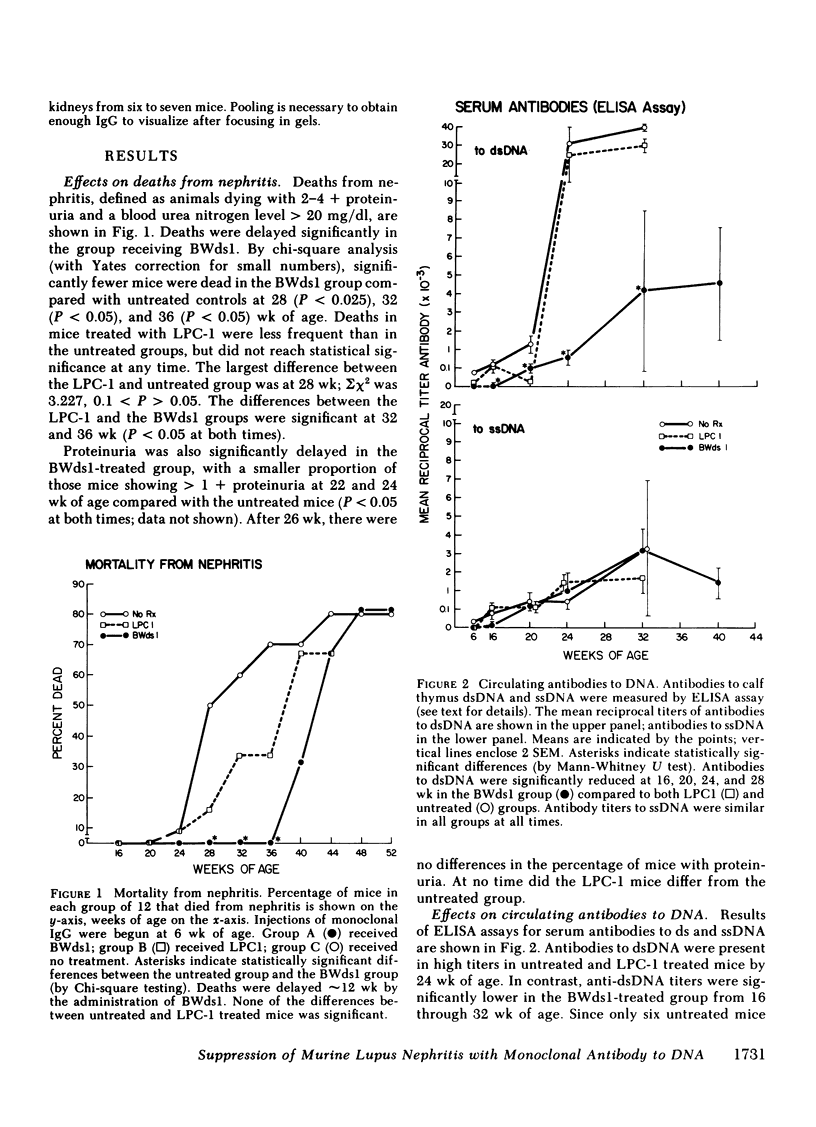
Suppression of circulating antibodies to double-stranded DNA was achieved in NZB/NZW f1 female mice by repeated administration of an IgG2a monoclonal antibody to DNA. Deaths from nephritis were delayed; glomerular deposition of IgG and of the cationic IgG DNA antibodies characteristic of murine lupus nephritis were diminished. Quantities of circulating antibodies to single-stranded DNA were not reduced compared with untreated or IgG myeloma-treated control mice. Antibodies directed against the monoclonal anti-DNA appeared in the circulation of treated mice after three inoculations of the idiotype. Those antibodies did not react with another monoclonal anti-DNA of the same allotype. One monoclonal anti-idiotypic antibody was obtained in hybridoma cultures derived from a spleen of a treated mouse. Cross-reactive or common idiotypes were found in 30-50% of NZB/NZW f1 sera and monoclonal DNA antibodies. Deletions of portions of the spectrotype of antibodies to DNA were found in sera containing anti-idiotypic antibodies, suggesting suppression of clones producing antibodies with isoelectric points similar to that of the immunizing idiotype. Deletions of some of the anti-idiotypic antibodies also occurred as the mice aged. Rheumatoid factors were not detectable in any sera. Therefore, administration of an antibody to DNA bearing an idiotype occurring with high frequency in NZB/NZW f1 females resulted in relatively specific suppression of the antibody response to double-stranded DNA, as well as suppression of nephritis. Reduction of anti-DNA synthesis by anti-idiotypic antibodies may have been an important suppressive mechanism. Experiments are in progress to test this hypothesis.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdou N. I., Wall H., Lindsley H. B., Halsey J. F., Suzuki T. Network theory in autoimmunity. In vitro suppression of serum anti-DNA antibody binding to DNA by anti-idiotypic antibody in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1981 May;67(5):1297–1304. doi: 10.1172/JCI110158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews B. S., Eisenberg R. A., Theofilopoulos A. N., Izui S., Wilson C. B., McConahey P. J., Murphy E. D., Roths J. B., Dixon F. J. Spontaneous murine lupus-like syndromes. Clinical and immunopathological manifestations in several strains. J Exp Med. 1978 Nov 1;148(5):1198–1215. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.5.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrzejewski C., Jr, Stollar B. D., Lalor T. M., Schwartz R. S. Hybridoma autoantibodies to DNA. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1499–1502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arana R., Seligmann M. Antibodies to native and denatured deoxyribonucleic acid in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1967 Nov;46(11):1867–1882. doi: 10.1172/JCI105677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asherson G. L., Zembala M., Gautam S. C., Watkins M. C. Control of suppressor cell activity: autoanti-idiotype B cells produced by painting with picryl chloride inhibit the T-suppressor cell which blocks the efferent stage of contact sensitivity. Cell Immunol. 1982 Jun;70(1):160–169. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90141-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton W. K., Schrock J. H., Davis J. S., 4th Rheumatoid factor inhibition of in vitro binding of IgG complexes in the human glomerulus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Mar;25(3):297–303. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briles D. E., Davie J. M. Detection of isoelectric focused antibody by autoradiography and hemolysis of antigen-coated erythrocytes. A comparison of methods. J Immunol Methods. 1975 Oct;8(4):363–372. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(75)90058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS J. S., 4th, BOLLET A. J. PROTECTION OF A COMPLEMENT-SENSITIVE ENZYME SYSTEM BY RHEUMATOID FACTOR. J Immunol. 1964 Jan;92:139–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daëron M., Couderc J., Ventura M., Liacopoulos P., Voisin G. A. Anaphylactic properties of mouse monoclonal IgG2a antibodies. Cell Immunol. 1982 Jun;70(1):27–40. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90130-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebling F., Hahn B. H. Restricted subpopulations of DNA antibodies in kidneys of mice with systemic lupus. Comparison of antibodies in serum and renal eluates. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Apr;23(4):392–403. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichmann K. Idiotype suppression. II. Amplification of a suppressor T cell with anti-idiotypic activity. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Aug;5(8):511–517. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichmann K., Rajewsky K. Induction of T and B cell immunity by anti-idiotypic antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Oct;5(10):661–666. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830051002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo G. R., Caulin-Glaser T., Lamm M. E. Charge of circulating immune complexes as a factor in glomerular basement membrane localization in mice. J Clin Invest. 1981 May;67(5):1305–1313. doi: 10.1172/JCI110159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn B. H., Ebling F., Freeman S., Clevinger B., Davie J. Production of monoclonal murine antibodies to DNA by somatic cell hybrids. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Aug;23(8):942–945. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerne N. K. Towards a network theory of the immune system. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1974 Jan;125C(1-2):373–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby K. S. Isolation and fractionation of nucleic acids. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1964;3:1–31. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60737-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffler D., Carr R., Agnello V., Thoburn R., Kunkel H. G. Antibodies to polynucleotides in human sera: antigenic specificity and relation to disease. J Exp Med. 1971 Jul 1;134(1):294–312. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.1.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Derivation of specific antibody-producing tissue culture and tumor lines by cell fusion. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jul;6(7):511–519. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafer E. M., Rauch J., Andrzejewski C., Jr, Mudd D., Furie B., Furie B., Schwartz R. S., Stollar B. D. Polyspecific monoclonal lupus autoantibodies reactive with both polynucleotides and phospholipids. J Exp Med. 1981 Apr 1;153(4):897–909. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.4.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion T. N., Lawton A. R., 3rd, Kearney J. F., Briles D. E. Anti-DNA autoantibodies in (NZB X NZW)F1 mice are clonally heterogeneous, but the majority share a common idiotype. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):668–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauch J., Murphy E., Roths J. B., Stollar B. D., Schwartz R. S. A high frequency idiotypic marker of anti-DNA autoantibodies in MRL-Ipr/Ipr mice. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):236–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley R. L., McGrath H., Jr, Taylor R. P. Detection of low avidity anti-DNA antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Mar;22(3):219–225. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothfield N. F., Stollar B. D. The relation of immunoglobulin class, pattern of anti-nuclear antibody, and complement-fixing antibodies to DNA in sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1967 Nov;46(11):1785–1794. doi: 10.1172/JCI105669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spring S. B., Nisonoff A. Allotypic markers on Fab fragments of mouse immunoglobulins. J Immunol. 1974 Aug;113(2):470–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sy M. S., Moorhead J. W., Claman H. N. Regulation of cell mediated immunity by antibodies: possible role of anti-receptor antibodies in the regulation of contact sensitivity to DNFB in mice. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2593–2598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talal N., Steinberg A. D. The pathogenesis of autoimmunity in New Zealand black mice. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1974;64(0):79–103. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65848-8_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Natali P. G. Comparative study of antibodies to native and denatured DNA. J Immunol. 1970 Apr;104(4):902–906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tron F., Charron D., Bach J. F., Talal N. Establishment and characterization of a murine hybridoma secreting monoclonal anti-DNA autoantibody. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2805–2809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodroffe A. J., Wilson C. B. An evaluation of elution techniques in the study of immune complex glomerulonephritis. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1788–1794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]