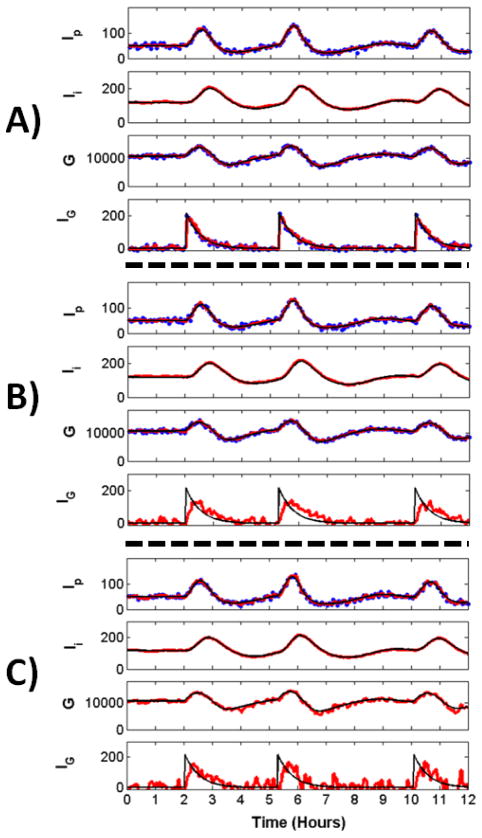
Fig. 1. Reconstruction of Glucose Model Dynamics.
Noisy measurements (blue) were recorded at 4 minute intervals and passed to the UKF framework to reconstruct all variables. Shown are the reconstructed (red) and true (black) dynamics for Ip, plasma insulin; Ii, remote insulin; G, glucose; and IG, the exogenous glucose delivery rate a.k.a the food intake. A) Reconstruction through the observation of Ip, G, IG. After a transient period (not shown), reconstructed dynamics remain close to true dynamics, even for the unobserved variable Ii. B) Reconstruction through the observation of Ip and G. Reconstruction is reasonably good for all hidden variables, notably for IG which receives no inputs from other variables. The estimate for IG is noisy compared to the estimate when this variable is observed. These perturbations do not affect the reconstruction fidelity of the rest of the system. C) Reconstruction through the observation of Ip alone. Reconstructed estimates are close to true dynamics. The estimate for IG is noisy, though the peaks representing food intake are clearly seen.