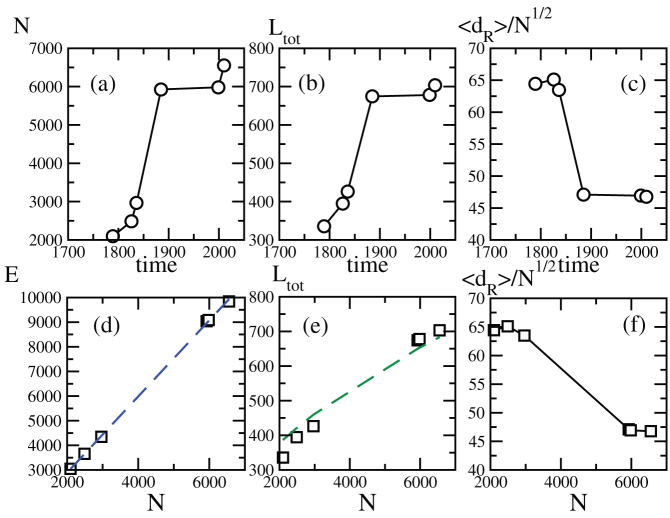
Figure 3.
Top panels: Number of (a) nodes, (b) total length (kms), and (c) rescaled average route distance versus time.Bottom panels: Number of (d) edges, (e) total length (kms), and (f) the rescaled average route distance versus the number of nodes N. In (d) the dashed (blue) line is a linear fit with slope 1.55 (r2 = 0.99) consistent with constant average degree of order 〈k〉 ≈ 3, and in (e) the dashed (green) line a square root fit of the form 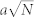 with a = 8.44 kms (r2 = 0.99). Based on a perturbed lattice picture this gives an area equal to
with a = 8.44 kms (r2 = 0.99). Based on a perturbed lattice picture this gives an area equal to 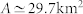 consistent with the actual value (A = 33.6 km2). In (f), we show the rescaled average shortest route versus N which decreases showing that the denser the network and the easier it is to navigate from one node to the other (if delays at junctions are neglected).
consistent with the actual value (A = 33.6 km2). In (f), we show the rescaled average shortest route versus N which decreases showing that the denser the network and the easier it is to navigate from one node to the other (if delays at junctions are neglected).