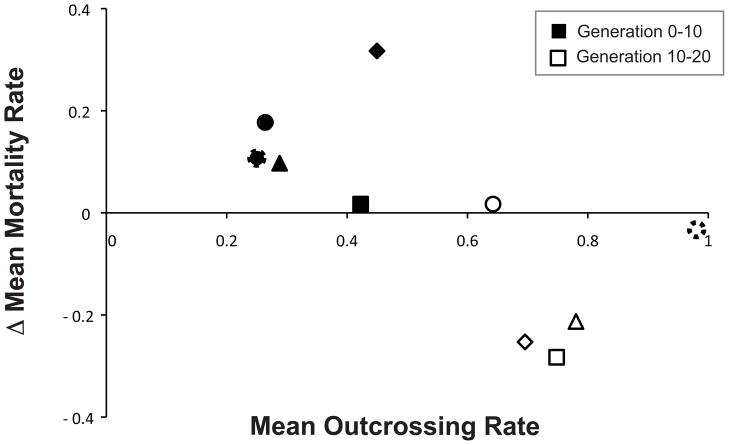
Figure 3.
Negative correlation between host outcrossing rate and change in host mortality in mixed mating populations. Elevated levels of outcrossing are generally correlated with decreases in host mortality rates (R2 = 0.435, F1,8 = 6.166, p = 0.0379). The harmonic mean outcrossing rate of each replicate population was plotted against the mean change in host mortality over two time periods, generations 0 to 10 (filled symbols) and generations 10 to 20 (open symbols), matching symbols indicate the same population measured at the different time points.