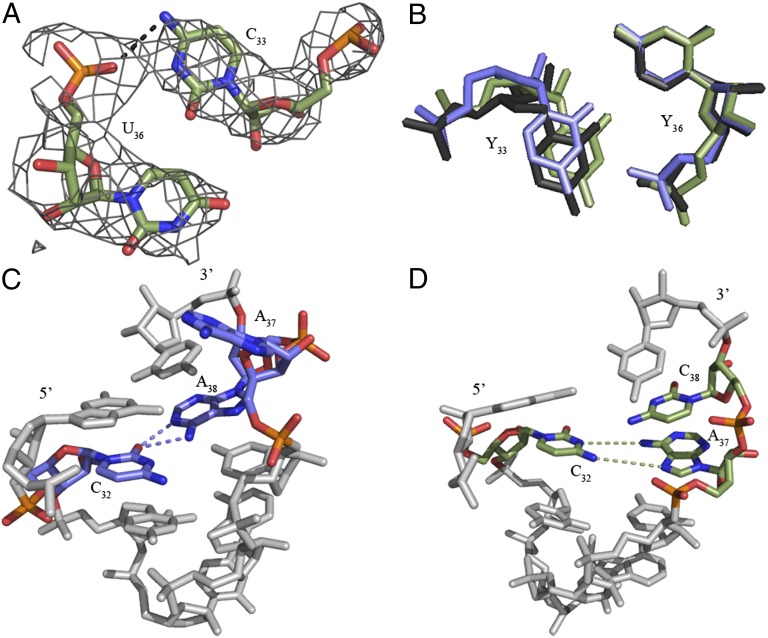
Fig. 2.
Unusual features of the 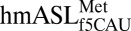 structure. (A) A hydrogen bond is able to form between C33N4 and the phosphate of U36. ASL carbons are colored green, and mRNA carbons are blue (m2FO-dFC contoured at 1.5 σ). (B)
structure. (A) A hydrogen bond is able to form between C33N4 and the phosphate of U36. ASL carbons are colored green, and mRNA carbons are blue (m2FO-dFC contoured at 1.5 σ). (B) 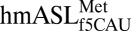 (green) is superimposed with E. coli elongator
(green) is superimposed with E. coli elongator 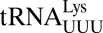 (blue) and human elongator
(blue) and human elongator 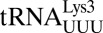 (black), showing a slightly distorted conformation. (C) In E. coli
(black), showing a slightly distorted conformation. (C) In E. coli
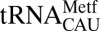 , the cross-loop interaction involves the familiar C32•A38 noncanonical base pair with A37 displaced from the loop, where it cannot participate in base stacking. (D) A cross-loop interaction in
, the cross-loop interaction involves the familiar C32•A38 noncanonical base pair with A37 displaced from the loop, where it cannot participate in base stacking. (D) A cross-loop interaction in 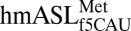 involves a unique interaction between C32 and A37 that consists of a base pair between the Watson–Crick edge of C32 and the Hoogsteen edge of A37.
involves a unique interaction between C32 and A37 that consists of a base pair between the Watson–Crick edge of C32 and the Hoogsteen edge of A37.