Figure 1.
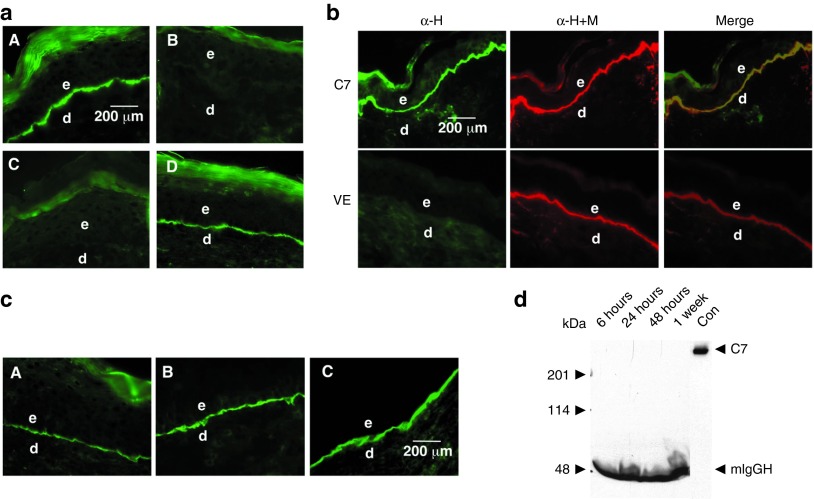
Topically applied rC7 stably incorporated in the regenerated DEJ in the mouse skin. (a) Immunofluorescence staining of the mouse skin was performed with an antibody specific for human C7 at 2 weeks after the topical application of 30 µg of rC7, NC1, or vehicle alone. Note that the healed wounds treated with rC7 (n = 30 mice) demonstrated a linear pattern of C7 deposition at the DEJ (panel A). In contrast, no human C7 was detected in mice treated with vehicle alone (n = 20 mice) or NC1 (n = 10 mice) (panels B and C). Panel D shows the stable incorporation of human rC7 at the mouse DEJ at 8 weeks after the initial topical application of rC7. (b) Immunofluorescence staining of mouse skin was performed 2 weeks after the topical application of rC7. The skin sections were labeled with either a monoclonal antibody specific for human C7 (green, panel α-H) or a rabbit polyclonal antibody that recognizes both mouse and human C7 (red, panel α-M+H). Merged images demonstrate colocalization of topically applied human rC7 with endogenous mouse C7 at the mouse DEJ. The lower panel depicts staining of wounds treated with the vehicle (VE) alone. (c) Dose-dependent deposition of human rC7 at the mouse DEJ after topical rC7 application. Immunofluorescence staining of biopsy specimens were performed with an antibody specific for human C7 after the animal's wounds were treated with 8 µg (A), 16 µg (B), or 32 µg (C) of topical rC7, respectively. Scale bar: 200 µm. (d) Sera were taken from mice at the time indicated after topically applied with 30 µg rC7 and subjected to 4–15% SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblot analysis using an anti-NC1 antibody. Purified rC7 of 10 ng was run as a control (Con). The positions of full-length 290 kDa C7, 50 kDa mouse IgG heavy chain (mIgGH), and molecular weight markers are indicated. d, dermis; e, epidermis.