Figure 6.
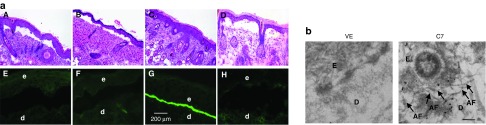
Topical application of rC7 incorporated into the DEJ of RDEB mouse skin grafts and forms AFs in vivo. (a) Histological appearance (A–D) and immunofluorescence staining (E–H) of engrafted RDEB mouse skin using a polyclonal antibody to the NC1 domain of C7. Panels A and E, 2 weeks after grafting of RDEB mouse skin and before treatment (n = 30 mice); panels B and F, wounded and engrafted RDEB skin 2 weeks after topically applied vehicle (n = 4 mice); panels C and G, wounded and engrafted RDEB skin 2 weeks after 30 µg of rC7 was applied topically (n = 15 mice); panels D and H, unwounded engrafted RDEB skin 2 weeks after 30 µg of rC7 was applied topically (n = 4 mice). (b) Immunogold labeling of engrafted murine RDEB skin topically applied with 30 µg rC7 (C7) or vehicle (VE) was performed using an anti-NC1 polyclonal antibody and revealed that the topical rC7 incorporated into the RDEB skin grafts and formed AFs. Note restoration of numerous arching AFs depicted with arrows and labeled with gold particles decorating the DEJ in rC7-treated RDEB skin grafts. AF, anchoring fibrils; d, dermis; e, epidermis; Scale bar: 100 nm.
