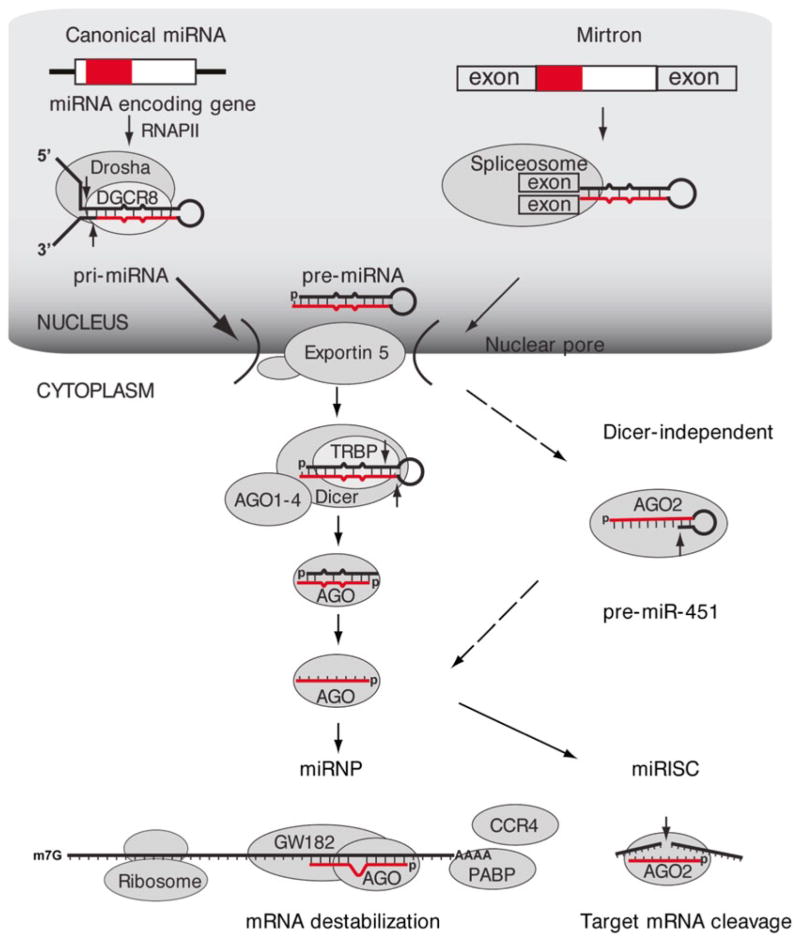
Fig. 1.1.
miRNA biogenesis pathway. miRNAs are transcribed by RNAPII to produce pri-miRNAs. Canonical miRNAs are processed by the endoribonuclease Drosha in partnership with its RBP partner DGCR8; mirtrons are instead processed by the spliceosome. The processed premiRNA is transported to the cytoplasm through an export complex consisting of exportin 5. The pre-miRNA is subsequently processed in the cytoplasm by another endoribonuclease Dicer in partnership with its RBP partner TRBP to form the final 21–23 nucleotide miRNA product. miR-451 is not processed by Dicer, but is rather cleaved by AGO2. Mature miRNAs (indicated in red) are then incorporated into AGO 1 through 4, forming miRNPs, also known as miRISC. miRNPs also incorporate other proteins, such as GW182. miRNPs are thought to direct miRNA mediated destabilization (i.e. through interaction with CCR4) or miRNA mediated translational repression (i.e. through interaction with ribosomes) of miRNAs without perfectly complementary mRNA targets. miRISC is thought to direct AGO2 catalyzed target mRNA cleavage of miRNA fully or nearly fully complementary mRNA targets