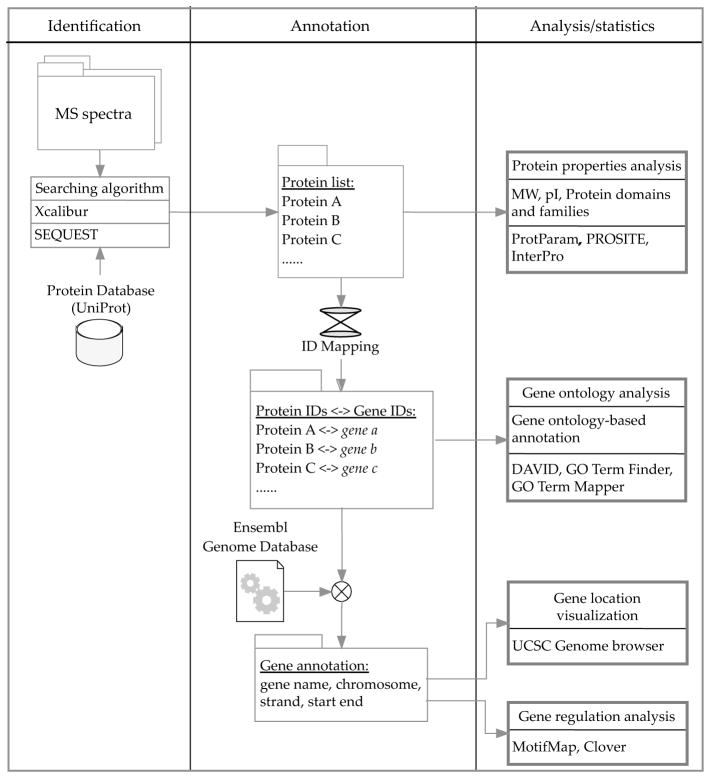
Figure 2. Flow chart for bioinformatic analysis of proteomic data.
Raw MS spectra are obtained from LC/MS/MS, and the results searched against a protein database (UniProt) using the SEQUEST algorithm, which is embedded in Xcalibur. This list can be used directly to obtain global features of the proteome, such as physical-chemical properties and protein domains/families. After converting protein identifiers to gene identifiers, gene ontology-based annotation can be conducted. The location of genes within chromosomes can be extracted from Ensembl genome database and visualized by UCSC genome browser. Candidate regulatory elements, i.e. binding motifs of transcription factors can be found using MotifMap database or Clover algorithm. Refer to Table 1 for the availability of these tools.