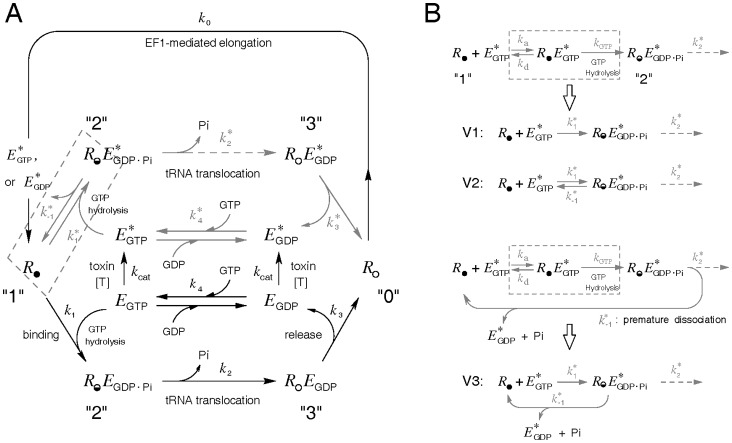
Figure 1. Schematics for the polypeptide chain elongation cycle.
(A) The ribosome is divided into four phases: the A-sites vacated POST phase R
O ready to receive a cognate aminoacyl-tRNA (phase “0”), the PRE phase 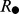 bearing a growing peptidyl-tRNA in the A site (phase “1”), the PRE ribosomal complex
bearing a growing peptidyl-tRNA in the A site (phase “1”), the PRE ribosomal complex 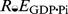 in transition of translocation (phase “2”), and the POST ribosomal complex R
O
E
GDP (phase “3”). Phases are interconnected by four reactions representing the EF1α-initiated peptide elongation (k
0), the combined factor binding and GTP hydrolysis (k
1), the EF2-mediated tRNA translocation (k
2), and EF2•GDP release (k
3). Reactions associated with ADPR•EF2 were depicted in gray, and the corresponding reaction rate constants distinguished by an asterisk superscript. (B) Model variations in the PRE ribosomal binding step and subsequent ADPR•EF2 turnover. The reversible factor binding and subsequent GTP hydrolysis are combined together as
in transition of translocation (phase “2”), and the POST ribosomal complex R
O
E
GDP (phase “3”). Phases are interconnected by four reactions representing the EF1α-initiated peptide elongation (k
0), the combined factor binding and GTP hydrolysis (k
1), the EF2-mediated tRNA translocation (k
2), and EF2•GDP release (k
3). Reactions associated with ADPR•EF2 were depicted in gray, and the corresponding reaction rate constants distinguished by an asterisk superscript. (B) Model variations in the PRE ribosomal binding step and subsequent ADPR•EF2 turnover. The reversible factor binding and subsequent GTP hydrolysis are combined together as 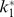 = k
a
k
GTP/(k
d+k
GTP). Three minor model variations are:
= k
a
k
GTP/(k
d+k
GTP). Three minor model variations are: 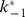 = 0 (model V1),
= 0 (model V1), 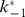 ≠ 0 and the dissociated factor is
≠ 0 and the dissociated factor is 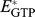 (model V2), and
(model V2), and 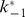 ≠ 0 and the dissociated factor is
≠ 0 and the dissociated factor is 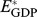 (model V3).
(model V3).