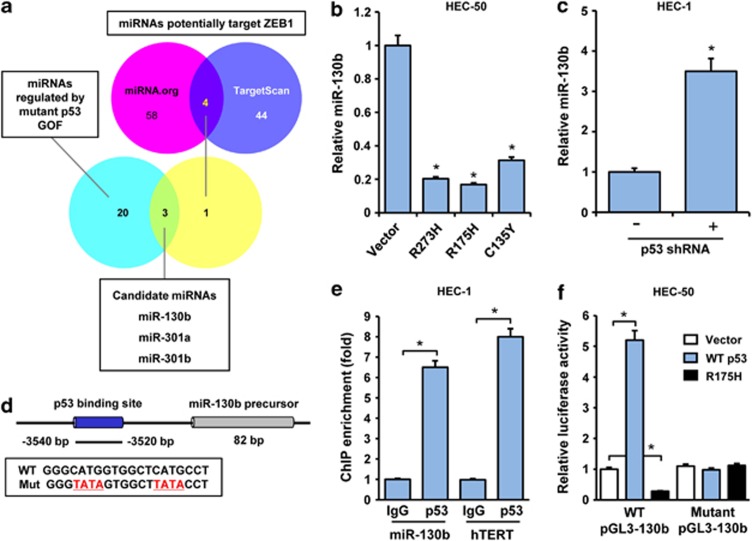
Figure 3.
Mutant p53 binds to and transrepresses the promoter of miR-130b. (a) Schematic of algorithm used to select candidate microRNAs that potentially target ZEB1, and are negatively regulated by mutant p53s. (b, c) Relative miR-130b expression levels in HEC-50 cells transfected with mutant p53 vector (b), or in HEC-1 cells after p53 silencing by shRNA (c), were determined by qRT–PCR (mean±s.d.; n=4; *P<0.01). (d) Location and sequence of predicted p53-binding sites in the promoter of miR-130b gene. Mutated residues (red) are indicated at the bottom. (e) ChIP–qPCR analysis of mutant p53 (DO-7 antibody) binding to the miR-130b promoter region in HEC-50 cells. Human telomerase (hTERT) was used as a positive control. The fold enrichment over the IgG control is represented (mean±s.d.; n=3; *P<0.01). (f) HEC-50 cells were transfected with luciferase reporter plasmid pGL3-130b or empty pGL3-basic vector, along with control vector, wild-type p53 or mutant p53 R175H vector, and relative luciferase activity were assayed (mean±s.d.; n=3; *P<0.01). All qRT–PCR or luciferase values were normalized to GAPDH or Renilla activity, respectively.