Abstract
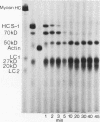
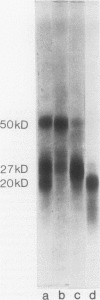
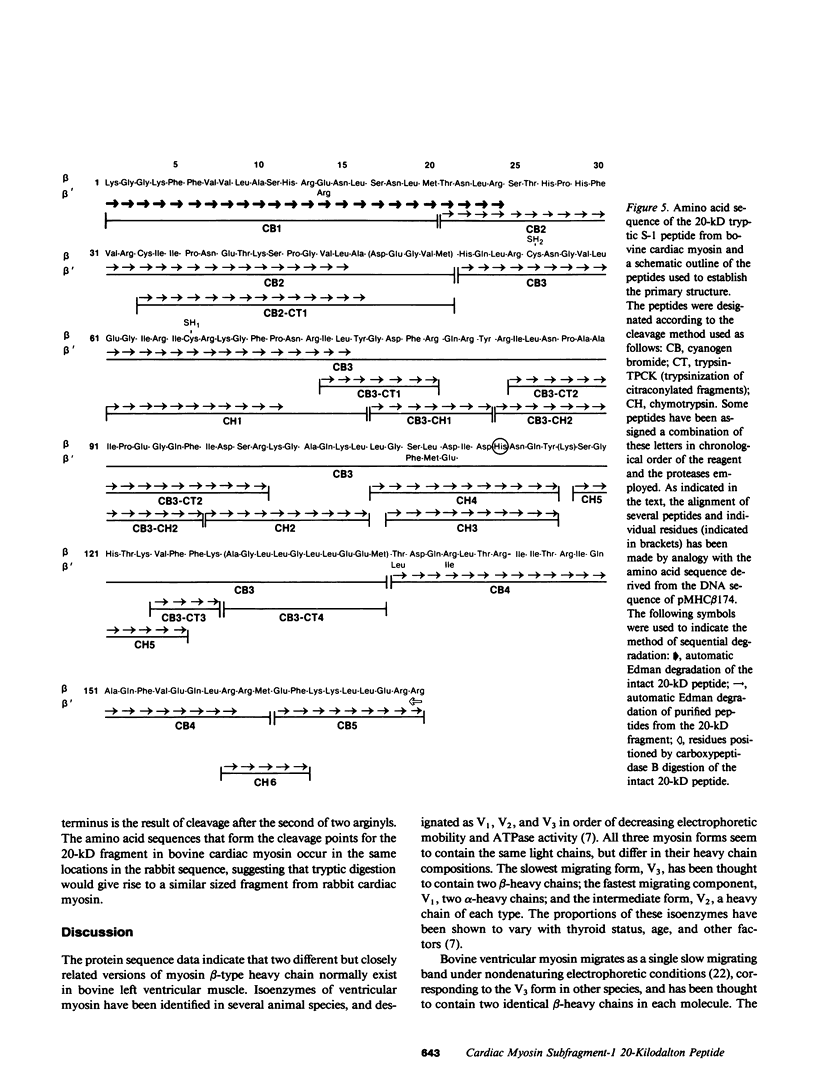
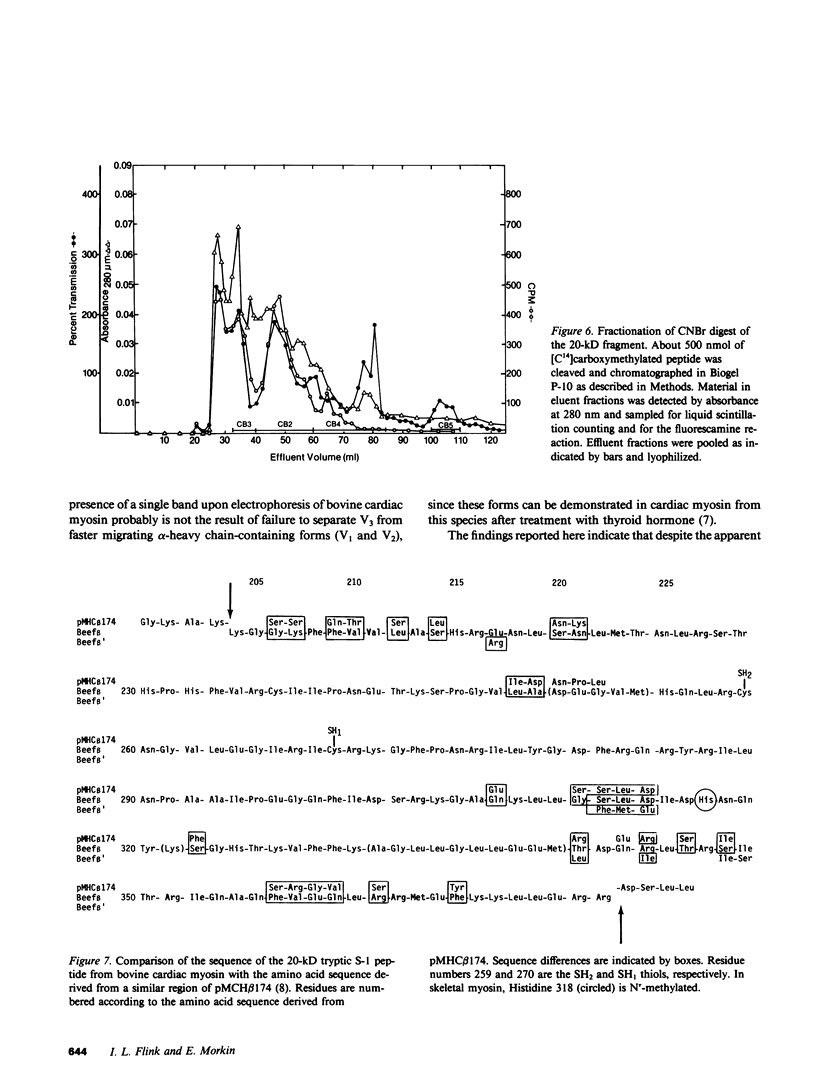
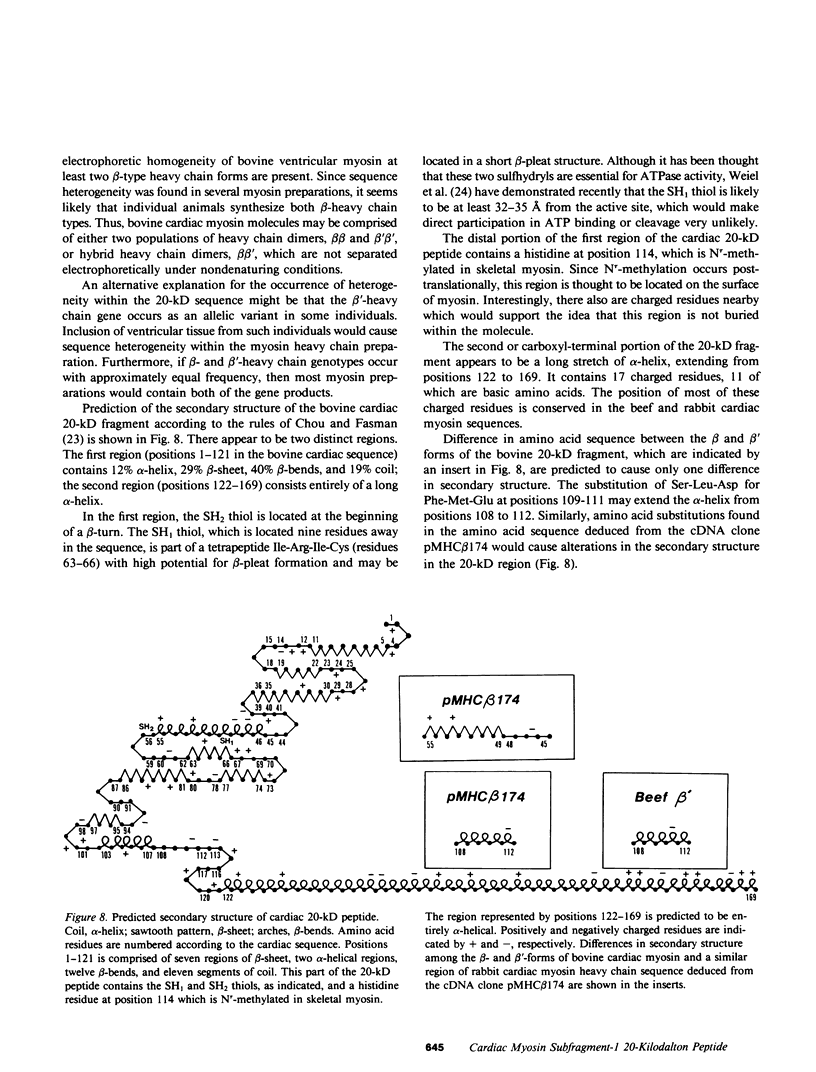
An almost complete amino acid sequence of the carboxyl-terminal 20-kD tryptic heavy chain peptide from bovine cardiac myosin Subfragment-1 (S-1) has been determined by automated sequential degradation of the undigested peptide and subfragments derived by chemical and enzymatic digestion. The fragment contains 169 residues, including two reactive cysteinyl residues which are located nine residues apart. At six positions in the sequence, two amino acid residues were present and two different versions of a chymotryptic peptide were isolated in approximately 53 and 24% yields, suggesting that there are two cardiac myosin beta-type heavy chains in this species. Analysis of the secondary structure of the 20-kD peptide predicts that there are two distinct regions within the fragment. The first region (residues 1-121) contains 12% alpha-helix, 25% beta-sheet, 40% beta-bends, and 19% coil; the second region (residues 122-169) may form an extended alpha-helix. Comparison of the bovine sequence with the deduced amino acid sequence of a recombinant plasmid containing DNA sequences coding for the beta-heavy chain of rabbit cardiac myosin (pMHC beta 174) reveals approximately 86% homology.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bálint M., Sréter F. A., Gergely J. Fragmentation of myosin by papain--studies on myosin from adult fast and slow skeletal and cardiac, and embryonic muscle. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Jun;168(2):557–566. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bálint M., Wolf I., Tarcsafalvi A., Gergely J., Sréter F. A. Location of SH-1 and SH-2 in the heavy chain segment of heavy meromyosin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Oct;190(2):793–799. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRESTFIELD A. M., STEIN W. H., MOORE S. Alkylation and identification of the histidine residues at the active site of ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jul;238:2413–2419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon H. B., Perham R. N. Reversible blocking of amino groups with citraconic anhydride. Biochem J. 1968 Sep;109(2):312–314. doi: 10.1042/bj1090312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flink I. L., Morkin E. Cyanogen bromide peptide from bovine cardiac myosin containing two essential thiols. Evidence for sequence homology with skeletal myosin in the region of the active site. FEBS Lett. 1977 Dec 15;84(2):261–265. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80702-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullmer C. S., Wasserman R. H. Analytical peptide mapping by high performance liquid chromatography. Application to intestinal calcium-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7208–7212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huszar G., Elzinga M. Homologous methylated and nonmethylated histidine peptides in skeletal and cardiac myosins. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 10;247(3):745–753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley A. F., Simmons R. M. Proposed mechanism of force generation in striated muscle. Nature. 1971 Oct 22;233(5321):533–538. doi: 10.1038/233533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inglis A. S., Nicholls P. W., Roxburgh C. M. Acid hydrolysis of phenylthiohydantoins of amino acids. Aust J Biol Sci. 1971 Dec;24(6):1247–1250. doi: 10.1071/bi9711247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kavinsky C. J., Umeda P. K., Levin J. E., Sinha A. M., Nigro J. M., Jakovcic S., Rabinowitz M. Analysis of cloned mRNA sequences encoding subfragment 2 and part of subfragment 1 of alpha- and beta-myosin heavy chains of rabbit heart. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):2775–2781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapper D. G., Wilde C. E., 3rd, Capra J. D. Automated amino acid sequence of small peptides utilizing Polybrene. Anal Biochem. 1978 Mar;85(1):126–131. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowey S., Slayter H. S., Weeds A. G., Baker H. Substructure of the myosin molecule. I. Subfragments of myosin by enzymic degradation. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 28;42(1):1–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90483-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney W. C., Hermodson M. A. Separation of large denatured peptides by reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography. Trifluoroacetic acid as a peptide solvent. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11199–11203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monken C. E., Gill G. N. Structural analysis of cGMP-dependent protein kinase using limited proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7067–7070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morkin E., Flink I. L., Goldman S. Biochemical and physiologic effects of thyroid hormone on cardiac performance. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1983 Mar-Apr;25(5):435–464. doi: 10.1016/0033-0620(83)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet D., Pantel P., Audemard E., Kassab R. The limited tryptic cleavage of chymotryptic S-1: an approach to the characterization of the actin site in myosin heads. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Aug 13;89(3):925–932. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91867-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry D. A. Structure of rabbit skeletal myosin. Analysis of the amino acid sequences of two fragments from the rod region. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 5;153(2):459–464. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90290-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. J., Neuberger M. R., Liu T. Y. Complete amino acid analysis of proteins from a single hydrolysate. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):1936–1940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha A. M., Umeda P. K., Kavinsky C. J., Rajamanickam C., Hsu H. J., Jakovcic S., Rabinowitz M. Molecular cloning of mRNA sequences for cardiac alpha- and beta-form myosin heavy chains: expression in ventricles of normal, hypothyroid, and thyrotoxic rabbits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5847–5851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takio K., Smith S. B., Walsh K. A., Krebs E. G., Titani K. Amino acid sequence around a "hinge" region and its "autophosphorylation" site in bovine Lung cGMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5531–5536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman C. L., Appella E., Pisano J. J. Rapid analysis of amino acid phenylthiohydantoins by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1977 Feb;77(2):569–573. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90276-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]