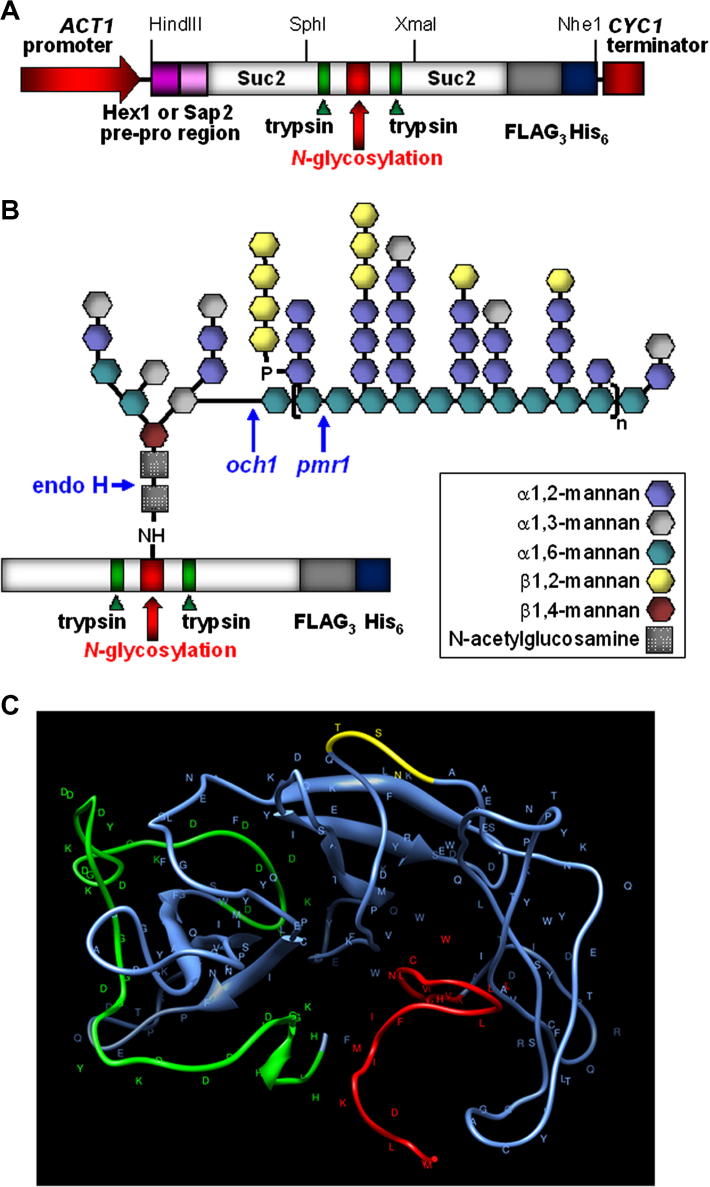
Fig. 1.
Design of the N-glycosylation reporters for C. albicans. (A) Cartoon illustrating the structure of the gene, which is transcribed from the ACT1 promoter and terminated via ScCYC1 sequences in pACT1 (Barelle et al., 2004). The codon optimised, synthetic coding regions encode part of the ScSuc2 protein which includes a single N-glycosylation site (Asn146-Ser-Thr) (Ziegler et al., 1988) flanked by trypsin cleavage sites. The synthetic coding regions encode carboxy-terminal FLAG3 and His6 tags. The GR1 reporter gene encodes an amino-terminal signal sequence from Hex1 (Cannon et al., 1994), whilst GR2 encodes an amino-terminal pre-pro-sequence from Sap2 (Morrison et al., 1993; Togni et al., 1991). GR3 is derived from GR2, but lacks the N-glycosylation site. (B) Cartoon illustrating the predicted structure of a mature N-glycosylated reporter protein, showing the glycosylation defects in C. albicans och1 and pmr1 mutants and the site of cleavage of endoglycosidase H (Netea et al., 2008). (C) Structural prediction of the GR1 reporter protein, highlighting the glycosylation site (yellow), the signal sequence (red), and the FLAG3-His6 tag (green).