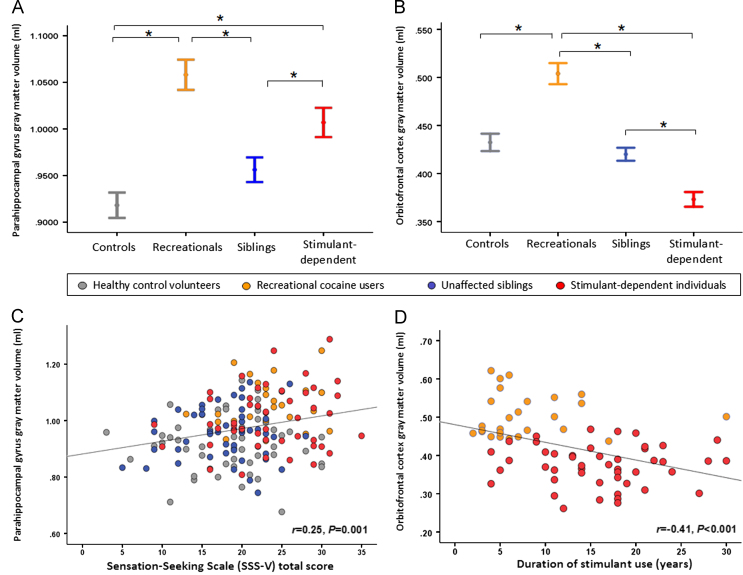
Figure 1.
Abnormalities in gray matter volume in recreational cocaine users and stimulant-dependent individuals (identified by comparisons with healthy control volunteers) were overlapping in the parahippocampal gyrus and the orbitofrontal cortex. (A) Parahippocampal volume was significantly increased in both drug user groups compared with control volunteers and also compared with the siblings. (B) The group difference in gray matter volume in the orbitofrontal cortex was due to recreational users showing a significant volume increase compared with healthy control volunteers and siblings, whereas orbitofrontal volume in the stimulant-dependent volunteers was significantly reduced compared with the other three groups. (C) Gray matter volume in the parahippocampal gyrus was associated with levels of sensation-seeking personality traits in all volunteers. (D) Relationship between orbitofrontal gray matter volume and stimulant use in recreational and dependent users: the longer individuals have been using stimulant drugs, the greater the decline in orbitofrontal volume. ⁎Significant post hoc comparisons following Bonferroni correction. SSS-V, Sensation-Seeking Scale-Form V.