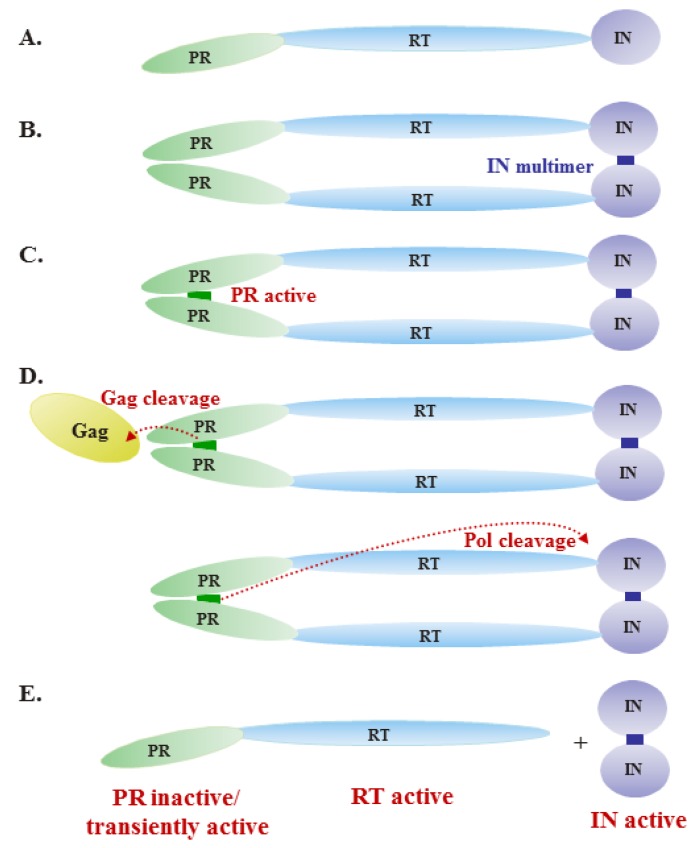
Figure 2.
Model of regulation of Pol enzymatic activities during virus assembly. (A) The precursor Pol protein contains the protease (PR), reverse transcriptase (RT) and integrase (IN) domains. (B) Upon incorporation into virions, the precursor Pol protein forms dimers through IN-IN interactions. (C) The dimerization of precursor Pol allows formation of the PR active site. (D) Active PR cleaves Gag and Pol proteins, as indicated by the dashed lines. (E) After cleavage, PR-RT remains a monomer and is active as a polymerase, initiating reverse transcription of the viral RNA genome. Free IN is also active.