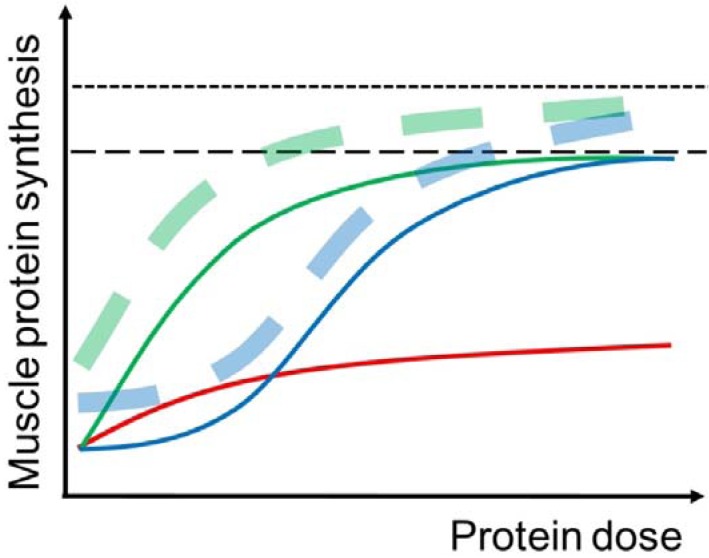
Figure 2.
Illustration of the muscle protein synthetic (MPS) response to protein intake at rest (solid curves) and with prior completion of resistance exercise (dashed curves) in young (green curves) and elderly (blue curves) individuals. In the young, MPS is stimulated already at small doses (~5 g) of protein intake and the response reaches a plateau at approximately 20 g of protein intake. In the elderly, a higher amount of protein intake is necessary to simulate MPS and to obtain the maximal MPS response. The MPS response to protein intake can be enhanced by prior completion of resistance exercise, although the effect of resistance exercise is somewhat reduced in elderly compared to young individuals. Furthermore, the red curve illustrates that the MPS response to protein intake is reduced in immobilized muscle.