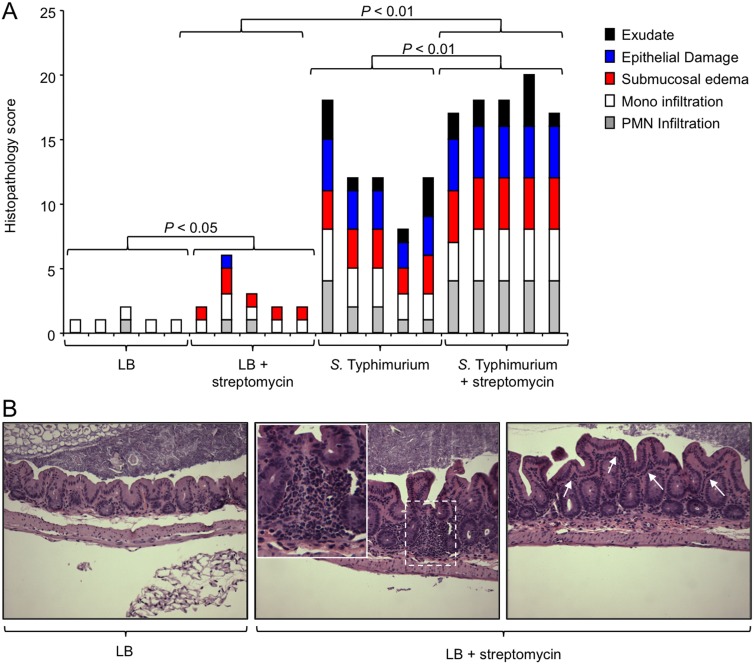
FIG 1 .
Streptomycin treatment is associated with a modest increase in the severity of histopathological changes. Mice received streptomycin or remained untreated. One day later, mice were inoculated with sterile medium (LB) or infected with S. Typhimurium. Three days after infection, their ceca were collected for analysis. (A) A veterinary pathologist performed blinded scoring of hematoxylin-eosin-stained sections of the cecal mucosa for histopathological changes. Each bar represents the combined histopathology score of one individual animal. The statistical significances of differences between groups are indicated above the brackets. (B) Representative images of sections from mice receiving LB (left) or LB plus streptomycin (middle and right). Arrows indicate mild diffuse inflammatory infiltrates in the lamina propria (right). A focal inflammatory infiltrate in the cecal mucosa is shown in the dashed square, and a larger magnification of this region is presented in the inset. Mono, monocyte; PMN, polymorphonuclear neutrophil.