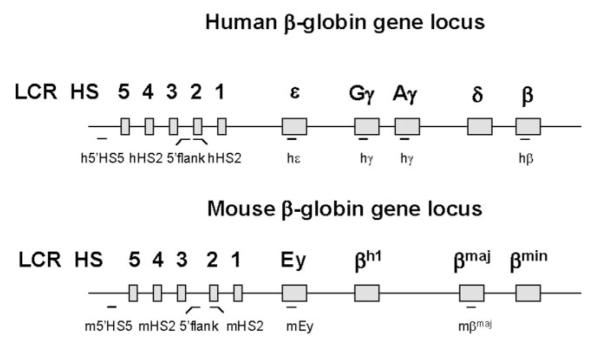
FIG. 1. Diagrammatic representation of the human and murine β-globin gene locus.
The human β-globin gene locus is located on chromosome 11 and consists of five developmentally regulated genes: the embryonic ∊-globin gene, the two fetal γ-globin genes, and the adult δ- and β-globin genes. The LCR is located upstream of the ∊-globin gene and is composed of at least five HS sites. The murine β-globin locus is located on chromosome 7 and contains four developmentally regulated genes: the Ey-and βh1-globin genes, which are co-expressed in the embryonic stage and the βmaj- and βmin-globin genes, which are expressed during the fetal and adult stages of erythropoiesis. The overall organization of the LCR is highly conserved between the murine and the human β-globin locus (2). PCR fragments analyzed in the ChIP experiments or used as probes in the NRO assays are indicated as lines (horizontal bars) below the respective loci.