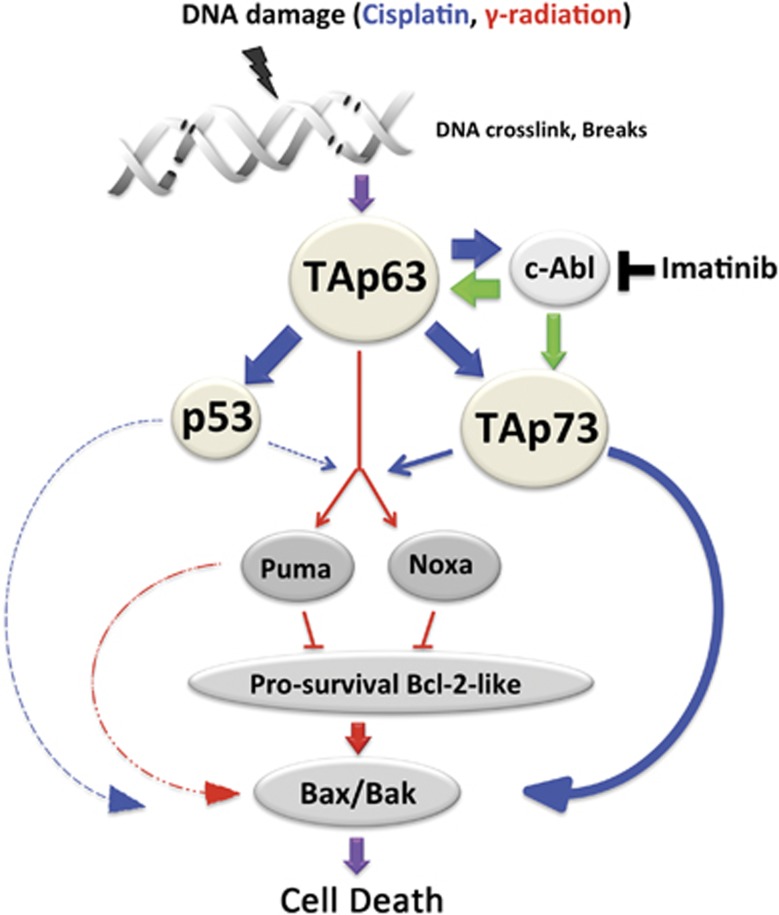
Figure 7.
Model for oocyte death regulated by p53 family members. All three p53 family members are involved in the apoptotic pathway in primordial follicle oocytes, with TAp63 playing a central role. DNA damage by γ-radiation activates signaling pathways through TAp63, resulting in the induction of Puma and Noxa and subsequent binding of PUMA and NOXA proteins to BAX/BAK as described in the recent report by Kerr et al. (red lines).23 DNA damage by cisplatin also activates TAp63, which results in upregulation of c-Abl. The kinase activity of c-Abl (green), which can be inhibited by imatinib, induces TAp63-dependent expression of TAp73 and subsequent degradation of TAp63. c-Abl may also activate TAp73 via phosphorylation; phospho-TAp73 then activates the apoptosis signaling pathway. p53 may have a minor or non-essential role in the activation of the apoptosis signaling pathway in response to cisplatin (shown as dotted line). The sequence of this signaling pathway and the consequences on primordial oocyte survival is profound and provides new insights into targets that may mitigate fertility loss in the cancer setting