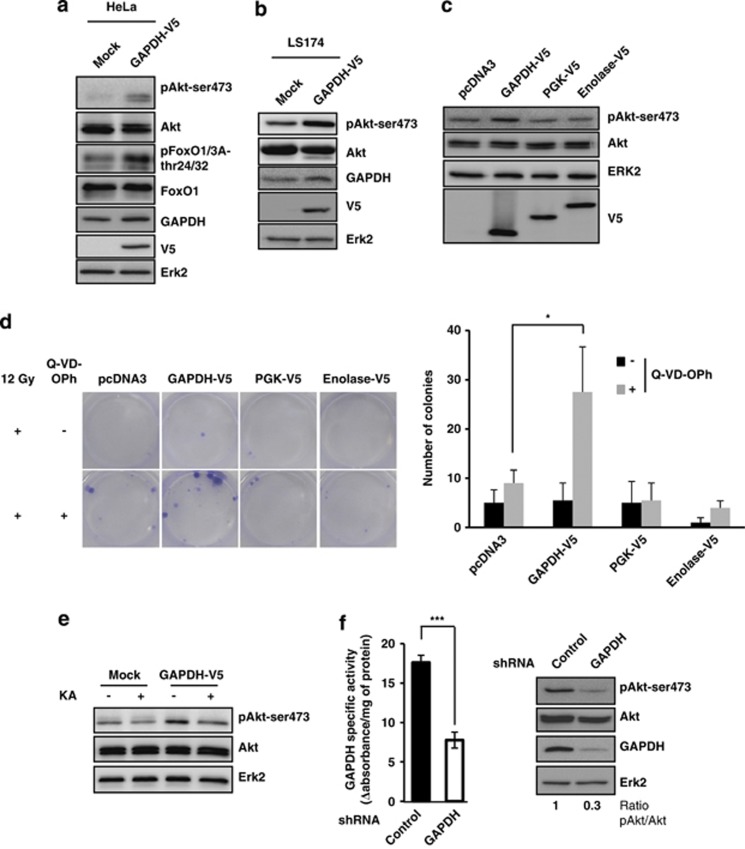
Figure 1.
GAPDH overexpression induces Akt pathway activation. (a) HeLa cells stably expressing a control pCDNA3 vector (Mock) or a GAPDH-V5-encoding pcDNA3 vector were immunoblotted for the indicated proteins (phospho- or total). (b) The levels of active phospho- and total Akt, GAPDH and V5 were assessed in the LS174 cell line stably expressing a control (Mock) or a GAPDH-V5-encoding vector. (c) HeLa cells were transiently transfected with the indicated encoding vectors and immunoblotted for the indicated proteins 48 h later. Expression of GAPDH-V5, PGK-V5 or enolase-V5 was assed using the V5 tag (bottom panel). (d) HeLa cells were transiently transfected with an empty vector (pcDNA3) or with pcDNA3 encoding GAPDH-V5, PGK-V5 or enolase-V5, and then irradiated as indicated±the caspase inhibitor Q-VD-OPh (20 μM). The caspase inhibitor was added 30 min before the irradiation (12 Gy) and replaced periodically at 48-h intervals for 10 days. Colonies were stained with crystal violet and assessed 18 days after treatment (left panel). The number of colonies counted under each condition for four independent experiments is shown in the right panel. (e) Mock or GAPDH-V5 HeLa cells were treated with 0.5 μg/ml KA for 6 h and Akt activation was assessed by immunoblots of phospho-(Ser473) and total Akt. (f) GAPDH specific activity (left), GAPDH protein level, and the level of active phospho- and total Akt (right) were assessed in HeLa cells transduced with either a control or an shRNA vector targeting GAPDH. The pAkt/Akt ratio was quantified and normalized to control cells. The immunoblots are representative of 3–5 independent experiments. Erk2 was used as a loading control *P<0.05, ***P<0.005