Abstract
Rapeseed-mustard oil is an essential dietary component, in India. The modification of rapeseed- mustard for fatty acid composition of seed oil to develop new genotypes having alternative oil and meal characteristics has been an important objective in quality breeding. Moreover, Breeding efforts in India are in progress to develop double low varieties to meet the internationally acceptable standards of oil and seed meal. So, information on the nutritional and anti-nutritional make-up of rapeseed-mustard oil and seed meal of the existing germplasm would be quite useful for the researchers especially breeders involved in the quality improvement programmes. In the present study database on biochemical characteristics of rapeseed-mustard has been developed using open source technology LAMP. The database provides the information on 14 important biochemical characters such as oil, saturated fatty acids, oleic, linoleic, linolenic, eicosenoic, erucic acid, monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA), polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), ω6/ω3 ratio, protein, glucosinolate, phenol, and fiber content. It offers web interface to submit and search data in the database. The database presently comprises biochemical characteristics of germplasm accessions, advance breeding lines and notified varieties of rapeseed-mustard. The database developed will be useful to the breeders in the selection of desired genotype with specific traits.
Keywords: Database, fatty acid profile, glucosinolate, LAMP, oil, protein, rapeseed –mustard
Background
Rapeseed-mustard is an important multipurpose perennial edible oil crop; today India produces almost 7.5 million tonnes of rapeseed-mustard from 6.5 million hectares area, becoming 3rd largest producer in world with a productivity of 1100 kilogram per hectare [1]. Rapeseed-mustard crops in India comprise traditionally grown indigenous species, namely toria (Brassica campestris L. var. toria), brown sarson (Brassica rapa L. var. brown sarson), yellow sarson (Brassica rapa L. var. yellow sarson), Indian mustard ([Brassica juncea (L.) Czernj & Cosson]), black mustard (Brassica nigra), taramira (Eruca sativa/vesicaria Mill.), gobhi sarson (Brassica napus L.) and Ethiopian mustard or karan rai (Brassica carinata A. Braun). The rapeseed-mustard oilseed is an important edible oilseed, having both the food and medicinal values. It is widely cultivated for the purpose of domestic consumption as well as export of seed meal. Strategic approaches are however, necessary for sustainable development of crop so to meet increasing demand of domestic consumption and international quality standards.
The rapeseed-mustard oil with high oleic acid and low linolenic acid imparts longer shelf life and is considered as good quality oil. Oil also should have high ratio of oleic to linoleic fatty acid and linoleic (ω-6) to linolenic (ω-3) fatty acid. High amount of erucic acid is not considered favorable for human consumption, therefore, development of commercial varieties free of erucic acid content in their oil and glucosinolates in meal is breeding objectives in this oilseed crop. Moreover phenol, fibre, phytate are another compounds which needs to be taken care in quality breeding. Improvement of genotypes to increase the production and quality of oil and seed meal is a challenging task for researchers. Information on the biochemical characteristics of rapeseed-mustard oil and seed meal would be quite useful for the researchers in traditional breeding and gene manipulation by using genetic engineering techniques. For this reason, the characterization of germplasm collections for seed oil and meal composition has special importance, with a view to identify potentially interesting genotypes.
DRMR (Directorate of Rapeseed-Mustard Research) holds the number of rapeseed-mustard species and being nodal agencies for rapeseed-mustard research in India, number of seed samples of germplasm accessions, breeding lines and notified varieties are being analysed for different biochemical characteristics from country wide and published in research papers, technical bulletins, research reports, etc. As Information on the biochemical characteristics of rapeseed-mustard is essential for improving the genotypes, therefore, need arises to maintain information on biochemical characteristics in an organized and accessible manner. This could be achieved by developing databases containing information similar to many other plant databases [2, 3, 4]. No specific online database is available which can be used as such for rapeseed-mustard crop that can meet the requirement of information retrieval need of local users as well as at the country level. In this sense, the present study was to design and develop a web based Biochemical Characteristics Database of Rapeseed-Mustard (BCDRM), which will empower in selection of desired genotype for certain traits.
The database contains the information on 14 important biochemical characters and offers Web interface to submit and Search data in the database. The database presently comprise records includes germplasm accessions, advance breeding lines and notified varieties of Rapeseed-Mustard crop. The broad objective of the work is to develop the web based database and provide the user-friendly interface to store, update and retrieve the biochemical information of rapeseed-mustard seed. Thus, BCDRMS is developed for the community of rapeseed-mustard researchers to facilitate, store, edit data and search for desired characteristics. The database has been developed using Open Source Technology LAMP and is accessible from any machine having web browser with internet connectivity.
Methodology
System design and development usually proceeds through several phases of software development life cycle (SDLC) that includes feasibility study (problem identification), requirement analysis (user's requirements), system design, testing, implementation and evaluation [5]. In general, users are not aware with, what to request and what really may facilitate and simplify their work. To find out requirements, the discussion sessions were organized with the possible users of the system i.e., researchers engaged in biochemical characterization, maintenance and use of crop genotypes at the DRMR, Bharatpur. After acquiring and collecting the necessary requirement information from the users, structuring the information and defining what really will facilitate the work of each of them is needed. Figure1 (A) is the use case diagram of the system.
Figure 1.
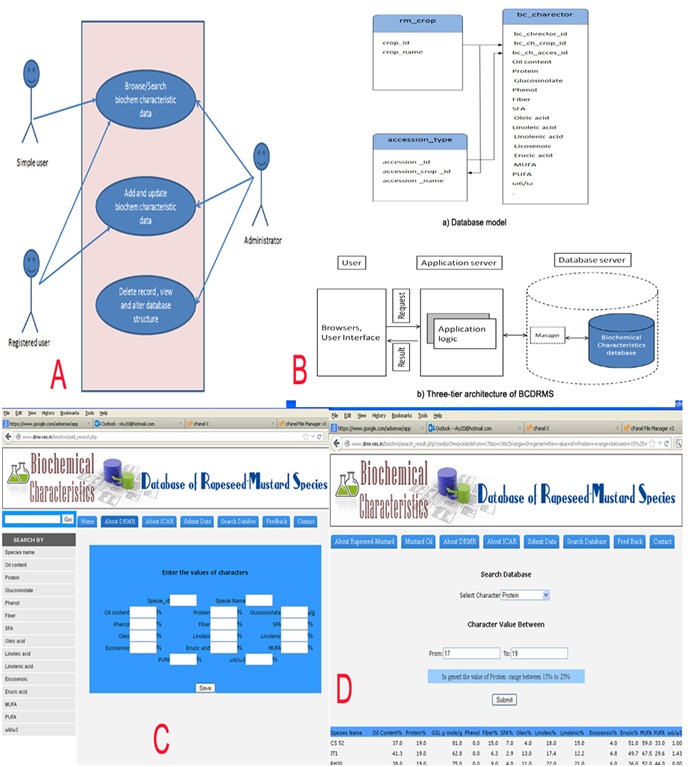
(A) Use case diagram of the system; (B) Database model and system design architecture; (C&D) Sample screen-shots provide the user interface.
System design and implementation:
The database model design and three tire system architecture designed to develop an efficient rapeseed-mustard Biochemical Characteristics Database is shown in Figure1 (B). The system architecture contains three layers namely, database, application and user interface. The database layer stores the data. Application logic layer was used to provide the interface between user and database. The queries are implemented in this layer for inserting, modifying and accessing data. The access rights are also specified in the application logic layer. Last is the user interface layer that contains the browser based platform to access the desired information from the database using an input entry forms. An open source platform consists of LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL and PHP) has been deployed with the standard web based three tier architecture to design and implement the system [6]. In BCDRM, the database has been created using MySQL database for storing the data in back-end, the Apache web server was used for bridging the gap between database server and user in retrieving the information remotely. PHP scripts are used to develop the dynamic web application, where the content displayed is generated from information accessed in a database. HTML is used in conjunction with PHP to give aesthetically pleasing web interface for users [7]. The hardware specifications include high end servers and storage devices.The system operates in sharing mode on a server running Linux kernel 2.6.18-194 operating system. MySQL version 5.1.56 and Apache 2.2.21 have been used for database management server and web server, respectively. PHP version 5.1.17 for server side scripting and Java script for client side scripting has been used in developing the system.
Results & Discussion
Database description:
The database contains the information on 14 important biochemical characters such as oil, protein, glucosinolate, phenol, fiber content, SFA, oleic, linoleic, linolenic, eicosenoic, erucic, MUFA, PUFA and ω6/ω3 ratio of different rapeseed-mustard genotypes. The database can be queried for the above mentioned characters. The BCDRMS is web based interactive user-friendly system that allows users without any specific training or knowledge of Structured Query Language (SQL) to perform record searches, insertions, updates, and deletions conveniently [8, 9]. Thus, researchers can perform remote database queries for search desired accessions of specific biochemical characteristics.
System Features:
The system operates in administrator and user mode. After login as administrator the INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE (IUD) of records can be performed. Searching is the key feature of any system, the BCDRM developed an user friendly interface to query the database. The result of query displays the matching records showing the different characters, by species name, the complete data for a particular accession can be viewed. Figure 1 (C&D), sample screen-shots provides the interface to insert records into the database and search desired information.
Utility
The database finds utility in rapeseed-mustard crop improvement. The database is freely available in public domain for searching character specific genotypes and authorized users are able to add, update records and maintain the database.
Conclusion & Further development
The BCDRM is a web based interactive user-friendly data base system that can be used by various users namely breeders, pathologists, extension professionals and farmers. The database contains the information on 14 important biochemical characters relating to rapeseed mustard. The user can access the system from any place. BCDRM is developed for the community of rapeseed-mustard researchers which will facilitate to store, edit data and search for desired characteristics. The database has been developed using Open Source Technology LAMP and is accessible from any machine having web browser with internet connectivity. It helps in finding the sources of rapeseed-mustard by identifying the most appropriate accessions with particular traits of interest.
Database updating, future work will continue to refine and incorporate existing in-house developed tools. BCDRM is accessible from http://www.drmr.res.in/ biochem/.
Footnotes
Citation:Kumar & Bala, Bioinformation 9(10): 537-540 (2013)
References
- 1.Chauhan JS, Jha SK. DRMR Vision 2030. Bharatpur, India: DRMR; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rajagopal, et al. Bioinformation. 2005;1:75. doi: 10.6026/97320630001075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ravisankar H, et al. Plant Genetic Resources. 2009;7:139. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Macas J, et al. Bioinformatics. 2002;18:28. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/18.1.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kumar, et al. Indian Research Journal of Extension Education. 2008;8:10. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Villordon A, et al. Hort Technology. 2007;17:567. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Meetei, et al. Bioinformation. 2012;8:209. doi: 10.6026/97320630008209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Jensen AL. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture. 2001;32:195. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Agrawal RC, et al. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture. 2007;59:90. [Google Scholar]


