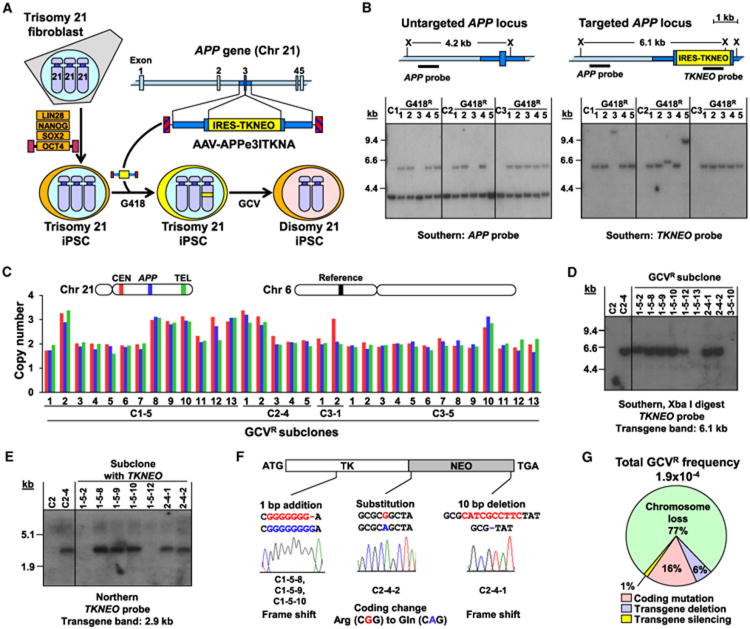
Figure 1. Targeting and Removal of Chromosome 21 from DS iPSCs.
(A) Schematic overview of experimental approach.
(B) Identification of chromosome 21 targeted clones. Maps of untargeted and targeted APP loci are shown. X, Xba I sites. The Southern blots show parental DS iPSC clones C1, C2, and C3 and their derived G418-resistant subclones after digestion with Xba I and being probed for APP or TKNEO.
(C) Copy numbers of three chromosome 21 loci and a chromosome 6 control locus were determined by quantitative Southern blots in 33 GCV-resistant subclones. Probe loci are shown in matched colors.
(D) TKNEO transgene presence in a subset of GCVR subclones as shown by Southern blot using a TKNEO probe. Parental trisomic iPSCs (C2) and targeted trisomic iPSCs (C2-4) were included as controls.
(E) Northern blot demonstrating TKNEO gene expression in a subset of the GCVR subclones containing TKNEO transgenes. Parental trisomic iPSCs (C2) and targeted trisomic iPSCs (C2-4) were included as controls.
(F) TKNEO coding region mutations found in the five GCVR subclones with expressed TKNEO transgenes. Wild-type sequences are shown above in red and mutant sequences are shown below in blue.
(G) Total frequency of GCV resistance and the percentage of GCVR subclones due to each type of event. See also Figure S1 and Tables S1 and S2.