Figure 2.
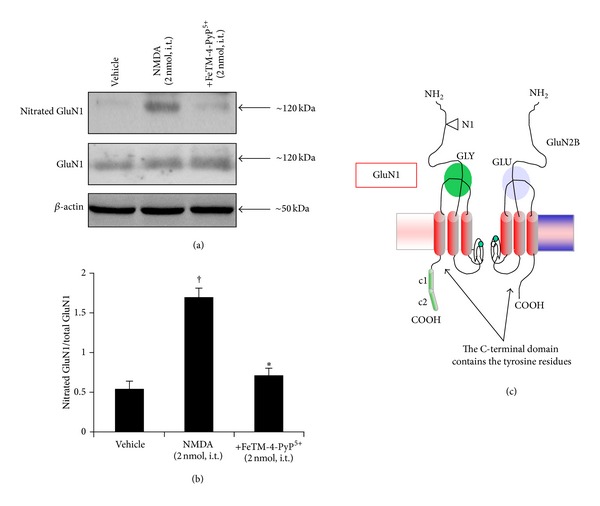
Inhibition of NMDA-induced hyperalgesia by FeTM-4-PyP5+ is associated with the inhibition of spinal protein nitration ((a)–(c)). As shown by immunoprecipitation, at the time of maximal NMDA mediated hyperalgesia (40 min), nitration of GluN1 was observed at the level of the spinal cord ((a), (b)). FeTM-4-PyP5+ (2 nmol given 15 min before NMDA) attenuates spinal GluN1 nitration ((a), (b)). Immunoprecipitation data shown in (a) are representative of at least 6 gels from 3 different animals performed on different days. Bar graph in (b) represents quantification by densitometric analysis. No difference for GluN1 or β-actin expression was detected among the lanes in these conditions. † P < 0.001 compared to vehicle and *P < 0.001 compared to NMDA alone.
