Figure 6. Sd and Tgi are required for ectopic apoptosis induced by hyperactive Hippo signaling.
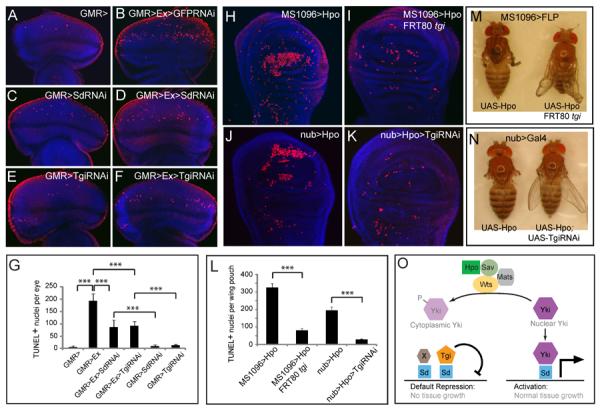
(A–G) Eye discs were stained for TUNEL (red) and DAPI (blue) (A–F), and TUNEL positive nuclei were quantified (G) (mean ± SEM, n=8). TUNEL positive nuclei in the whole eye disc were counted by projecting a Z-stack of serial confocal optical sections into one focal plane. *** denotes a p-value < 1.5E-5. The complete genotypes are: (A) UAS-Dicer2; GMR-Gal4; (B) UAS-Dicer2; GMR-Gal4 UAS-Ex; UAS-GFPRNAi; (C) UAS-Dicer2; GMR-Gal4; UAS-Sd RNAi; (D) UAS-Dicer2; GMR-Gal4 UAS-Ex; UAS-SdRNAi; (E) UAS-Dicer2; GMR-Gal4/UAS- TgiRNAi; (F) UAS-Dicer2; GMR-Gal4 UAS-Ex/UAS-TgiRNAi.
(H–L) Wing discs were stained for TUNEL and DAPI (H–K) and TUNEL positive nuclei in the wing pouch region was quantified by Z-stack projections of confocal sections (L). The complete genotypes are: (H) MS1096-Gal4 UAS-Flp; UAS-Hpo; (I) MS1096-Gal4 UAS-Flp; UAS-Hpo; FRT80BtgiΔP/FRT80 RpS17; (J) UAS-Dicer2; nub-Gal4/UAS-Hpo; (K) UAS-Dicer2; nub-Gal4/UAS-Hpo; UAS-TgiRNAi. (L) shows quantification of TUNEL-positive nuclei in the wing pouch (mean ± SEM, n=8). *** denotes a p-value < 2.5E-5.
(M) and (N): Adult flies corresponding to animals analyzed in (H–I) and (J–K), respectively. Note the extremely reduced wing size in flies expressing UAS-Hpo by MS1096-Gal4 or nub-Gal4 (animal to the left; showing tiny wing remnants), and the appreciable wing size of flies in which Hpo overexpression was combined with loss of Tgi (animal to the right).
(O) A model for how Hippo signaling switches Sd between Tgi-mediated repression and Yki-mediated activation. Additional Sd co-repressors (protein X in the diagram) likely exist since Tgi plays a partial role in Sd-mediated default repression in the eye disc. See text for details.
See Figure S6 for data supplemental to Figure 6.
