Figure 1.
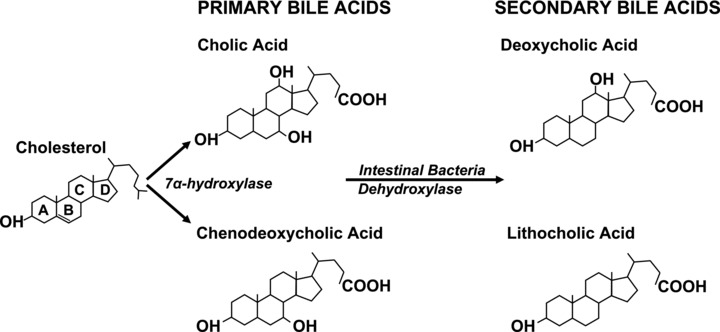
This scheme shows the structure of major human BAs derived from cholesterol metabolism. The steroid nucleus and ring lettering for both primary and secondary human BAs are shown. Dehydroxylases derived from intestinal bacteria regulate formation of secondary BAs. The degree of hydroxylation of the steroid nucleus determines the biochemical and functional characteristics of both primary and secondary BAs. Whereas cholic acid has three hydroxyl groups, chenodeoxycholic acid and deoxycholic acid have two, and lithocholic acid has one.
