Fig. 1.
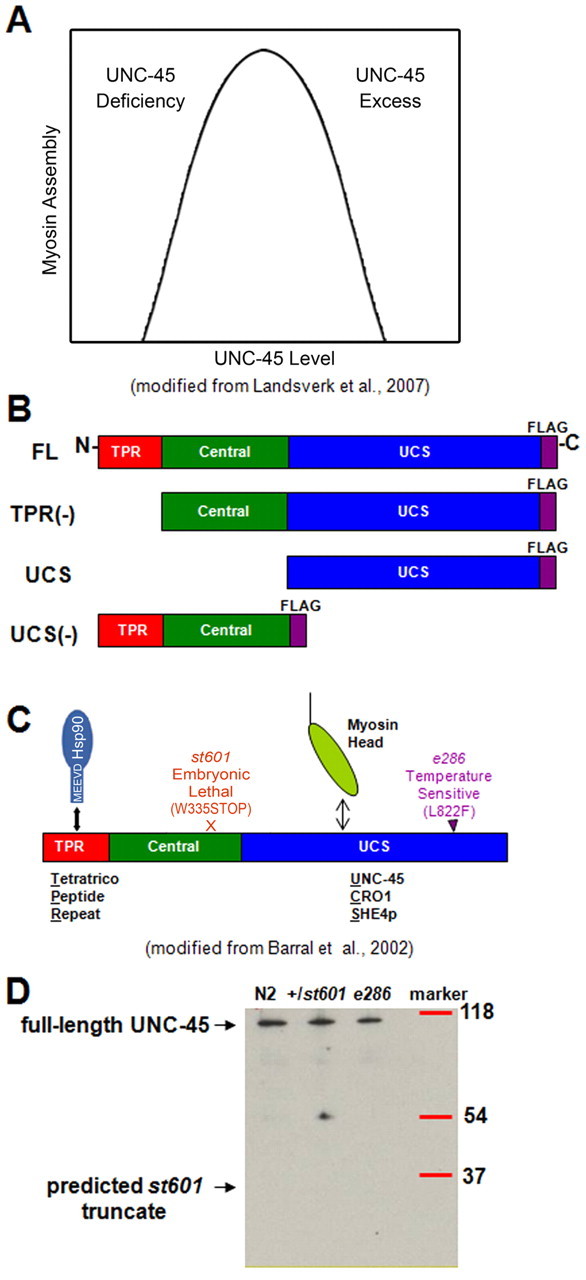
UNC-45 is a multifunctional protein consisting of three identifiable regions. (A) Model of myosin assembly dependence on UNC-45 protein levels in C. elegans body-wall muscle cells. Myosin heavy chain accumulation and its consequent assembly are controlled by protein degradation on either side of the optimal UNC-45 concentration range (Hoppe et al., 2004; Landsverk et al., 2007). (B) Fragments cloned for injection under control of the body-wall muscle-specific unc-54 promoter with the FLAG tag on the C-terminus. (C) UNC-45 contains the N-terminal Hsp90-binding TPR domain, the central region and the C-terminal myosin-binding UCS domain (Barral et al., 1998; Barral et al., 2002). The arrows show the location of the embryonic lethal mutation st601 and the temperature-sensitive mutation e286. (D) The st601 mutation does not produce the predicted truncated protein fragment. st601 UNC-45 protein was examined in heterozygous st601, N2 and e286 worms by immunoblots with rabbit polyclonal anti-C. elegans UNC-45 antibody.
