Fig. 5.
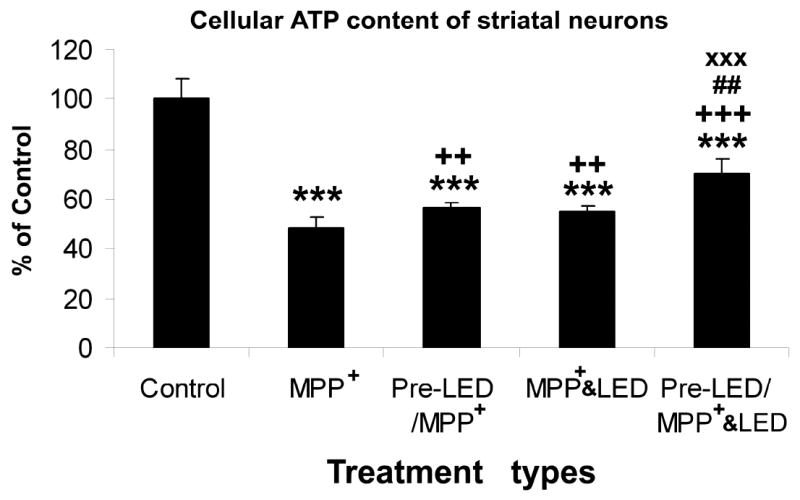
Effect of LED treatment and pre-treatment on cellular ATP content in striatal neurons exposed to 250 μM MPP+. MPP+ severely reduced ATP content from control levels (P < 0.001). Either LED treatment or pretreatment was effective in increasing ATP content above that of MPP+ alone (P < 0.01), and there was no significant difference between the two groups. However, LED pretreatment plus LED treatment during MPP+ exposure was most beneficial in increasing ATP content of striatal neurons (## P < 0.01 in comparison to pre-LED/ MPP+, and XXX P < 0.001 in comparison to MPP+ & LED).
All “* P” values were compared to controls: ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001. All “+P” values were compared to MPP+ or rotenone alone: ++ P < 0.01, +++ P < 0.001. All “#P” values compared “LED pretreatment plus LED treatment during toxin exposure group” to “LED during toxin exposure only group”. Scale bar: 25 μm for all.
