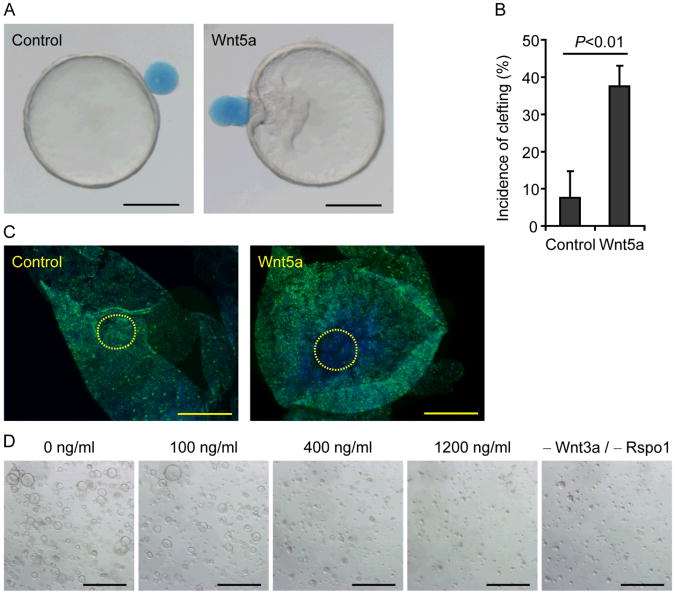
Fig. 3.
Wnt5a inhibits proliferation of colonic epithelial stem cells. (A) Focal Wnt5a-induced clefts in colonic epithelial organoids. A control (left panel) or a Wnt5a-soaked bead (right panel) was placed adjacent to different colonic organoids. Bars, 200 μm. (B) Plot of the mean cleft incidence of colonic organoids (+ SD) attached to control or Wnt5a-soaked beads (n=3 experiments). A Student's t-test was used to determine significance. (C) Colonic organoids attached to either control (left panel) or Wnt5a-soaked beads (right panel) were stained for Ki-67 (green). Yellow dotted lines outline the bead attachment area. Nuclei were counterstained with bis-benzimide (blue). Representative images from 3 samples (per group) were shown. Bars, 200 μm. (D) Representative images of colonic epithelial organoids cultured for 48 hours in indicated conditions (n=3 experiments). Bars, 500 μm.