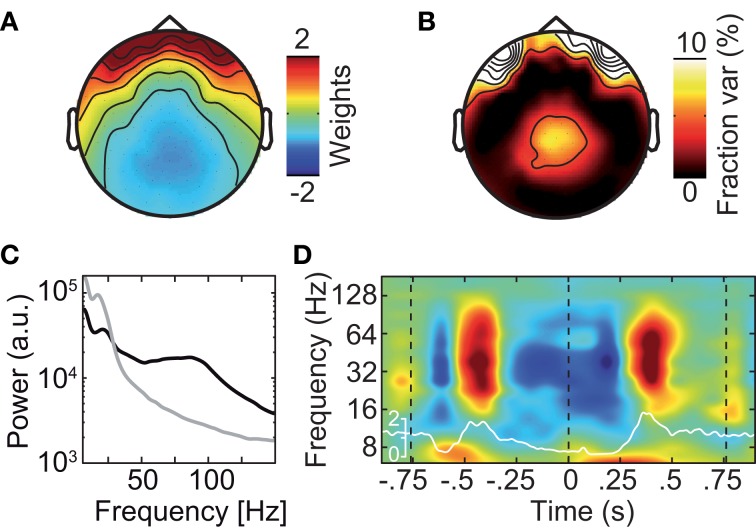
Figure 6.
Exemplary independent component (IC) that captures the saccadic spike artifact. (A) Scalp topography of the saccadic spike IC. (B) Scalp topography of the fraction of signal power explained by the saccadic spike IC. (C) Power spectrum of the saccadic spike IC (black) and average power spectrum of all physiological (i.e., non-muscle) ICs (gray). (D) Change in the saccadic spike ICs' signal power relative to prestimulus baseline resolved in time and frequency. The white line shows the concurrent microsaccade rate for comparison (compare Figure 5A).