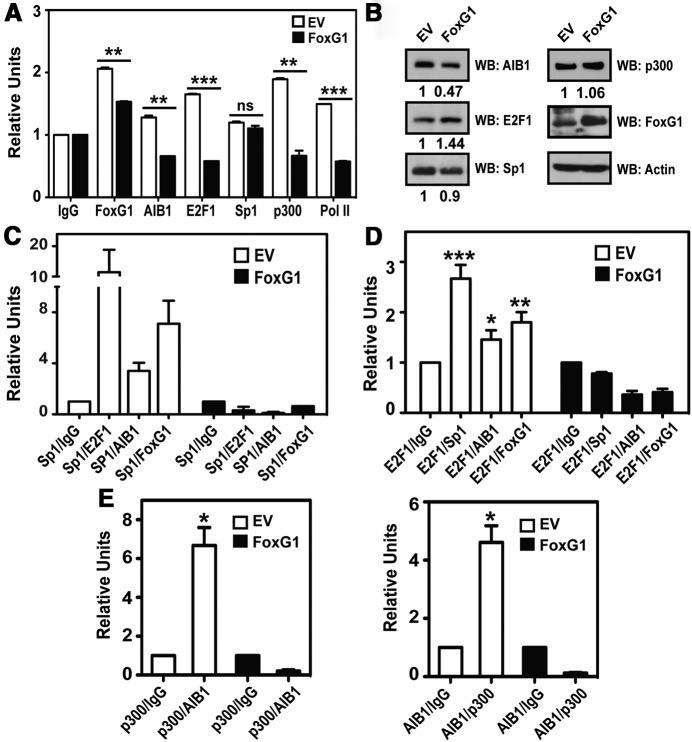
Figure 5.
FoxG1 Destabilizes the Sp1-Associated Transcription Complex on the AIB1 Gene Promoter. A, FoxG1 overexpression leads to decreased recruitment of the members of the transcriptional complex to the endogenous AIB1 promoter. ChIP assays were performed in MCF-7 cells transfected with EV or FoxG1 vectors, by enriching protein-bound endogenous AIB1 promoter with antibodies as indicated. Student's t test, in which ***, P < .001; **, P < .01 were FoxG1-expressing cells (black bars) relative to EV (white bars). B, Relative protein levels after FoxG1 transfection in MCF-7 cells are shown by WB and probed with antibodies as indicated. C and D, Overexpressing FoxG1 compromises the integrity of the transcription complex. The immunocomplexes associated with the AIB1 promoter were assessed by reChIP experiments, where chromatin was immunoprecipitated sequentially first with an anti-Sp1 antibody, followed by reChIP with antibodies specific to either E2F1, AIB1, or FoxG1; or first with an anti-E2F1 antibody, followed by reChIP with antibodies specific to either Sp1, AIB1, or FoxG1. The Sp1-ChIP and E2F1-ChIP were also followed by a reChIP of IgG as a negative control. ***, P < .001; **, P < .01; *, P < .05 relative to E2F1/IgG. Student's t test. E, Overexpressing FoxG1 causes reduction in p300-AIB1 co-occupancy at the AIB1 promoter. MCF-7 cells were transfected with EV or FoxG1 as in panel A and harvested for reChIP experiments by performing reciprocal and sequential ChIPs using antibodies specific to p300, followed by AIB1, or to AIB1, followed by p300. The AIB1 promoter-specific primers were used to assess the relative occupancy of the AIB1–p300 complex at the endogenous AIB1 promoter. *, P < .05 relative to p300/IgG or AIB1/IgG. Student's t test.