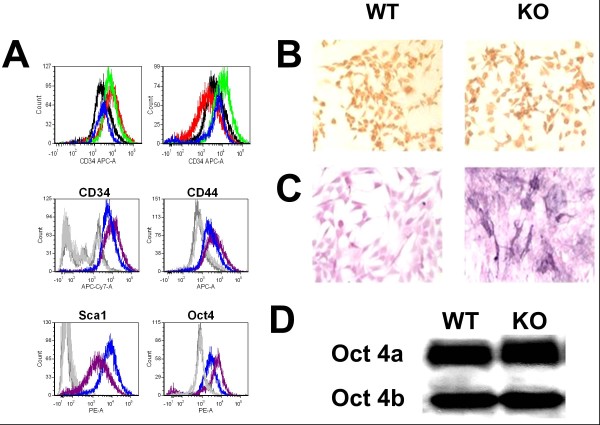
Figure 1.
Effect of genetic inactivation of myostatin on the expression of key stem cell marker genes in MDSC. (A) Flow cytometry (no gate) was conducted for Sca1 (red), CD34 (black), CD44 (green), and Oct 4 (blue) in WT MDSCs (blue) and Mst KO MDSCs (purple), against the respective isotypes (not shown). Top panels: Left: WT MDSCs; Right: Mst KO MDSCs. Bottom panels: each antigen is compared separately for WT (blue) and Mst KO (purple), with the corresponding isotypes (WT, dark gray; Mst KO, light gray). (B) Representative pictures of proliferating MDSCs that were subjected to immunocytochemistry for Oct 4, showing nuclear location in most cells (200×). (C) Proliferating MDSCs that were subjected to cytochemistry for alkaline phosphatase (200×). (D) Homogenates from the same cell cultures that were subjected to Western blot for Oct 4 (nuclear Oct 4a, 45 kDa; cytoplasmic Oct 4 b, 33 kDa). WT, wild type; MDSC, muscle-derived stem cell; Mst KO, myostatin knockout.