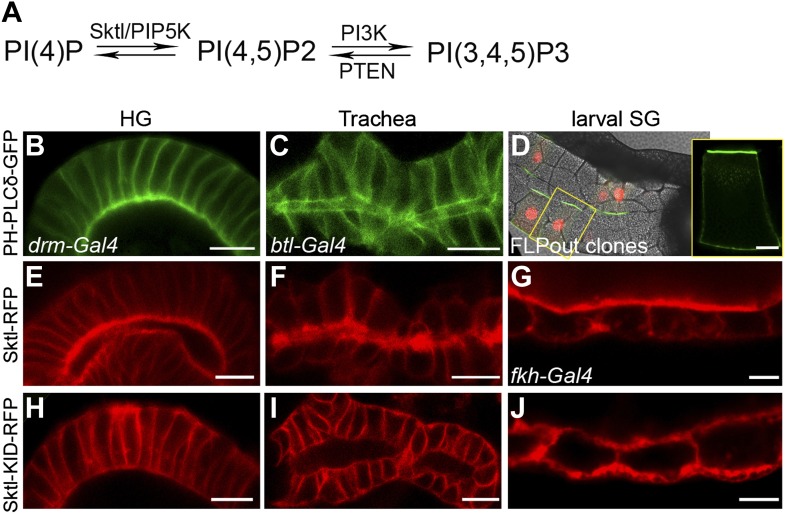
Figure 4. PI(4,5)P2 and Skittles, a PIP5 kinase, are apically enriched in Drosophila tubular organs.
(A) Simplified scheme of the PI(4,5)P2 biosynthetic pathway. PI(4)P is phosphorylated by Sktl /PIP5K to generate PI(4,5)P2. PI(4,5)P2 can be further phosphorylated by PI3K to produce PI(3,4,5)P3, which can be dephosphorylated by PTEN phosphatase to regenerate PI(4,5)P2. (B–D) Live imaging of PH-PLCδ-GFP following expression in stage 14 embryonic hindgut (B) and trachea (C) under drm-Gal4 and btl-Gal4, respectively, and in third instar larval salivary gland FLP-out clones (D). (D) Salivary gland FLP-out clones expressing PH-PLCδ-GFP under actin-Gal4. Clones are marked by nuclear RFP (red), and the salivary gland outline is visualized using transmitted light. Inset shows sensor distribution within a single magnified clone cell. PH-PLCδ-GFP is enriched at the apical surface of these tubular organs. (E–J) Live imaging of Sktl-RFP and Sktl-KID-RFP, following expression in the embryonic hindgut (E and H) and trachea (F and I) under drm-Gal4 and btl-Gal4, respectively, and in the 2nd instar larval salivary gland under fkh-Gal4 (G and J). Sktl is enriched at the apical domain, while a kinase-dead form (Sktl-KID) is localized throughout the cell cortex. Scale bars, 10 μm, and 20 μm (D).