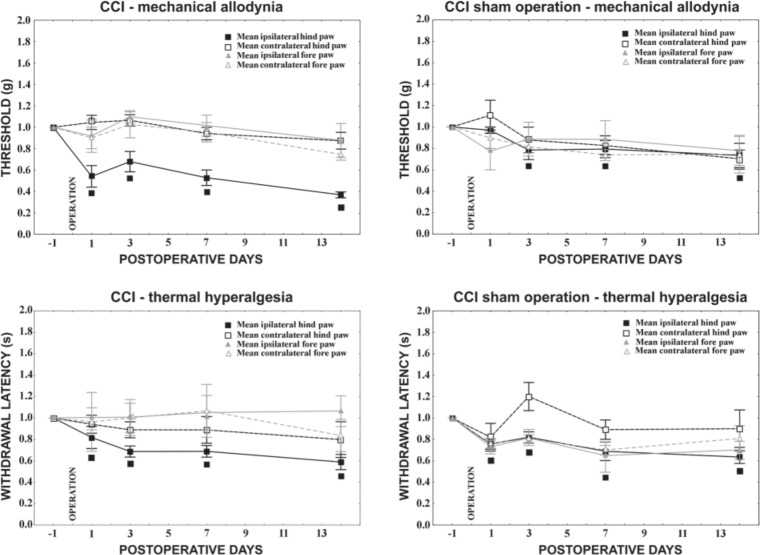
Figure 1.
Behavioral tests in chronic constriction injury (CCI) and sham-operated rats. CCI operation evoked mechanical allodynia as well as thermal hyperalgesia in the ipsilateral hindpaw starting the first day from surgery. Sham-operated rats also exhibited both mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia in ipsilateral hindpaws, albeit less so than did the CCI animals. No signs of neuropathy were observed in forepaws either after mechanical or thermal stimuli. Data are expressed as mean ± standard error of withdrawal thresholds in grams and withdrawal latency in seconds for mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia, respectively. The threshold index and index of withdrawal latency indicate the ratio of after-surgery measurement to measurement before operation. ■ Indicates statistically significant difference of ipsilateral hindpaw values after CCI when compared with the measurement in naive animals (p<0.05).