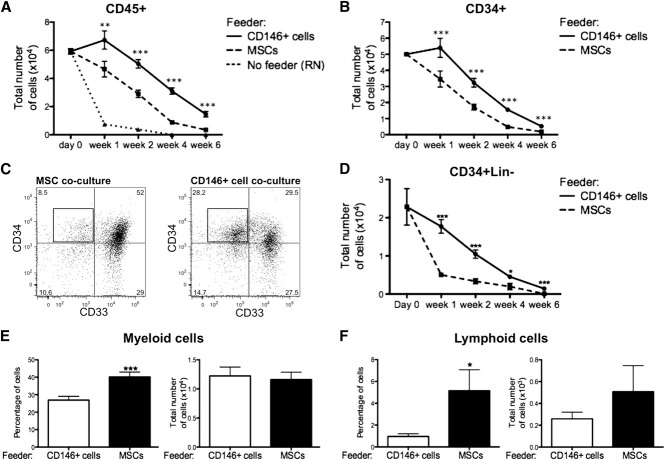
Figure 4.
CD146+ perivascular cells promote ex vivo maintenance of undifferentiated HSPCs. (A) In the absence of cytokines and stromal cell feeder layer (No feeder), CD45+ hematopoietic cells cultured in RN-treated wells rapidly died within the first 2 weeks of culture. At any time of culture, the total number of CD45+ cells recovered from CD146+ cell cocultures was significantly higher when compared with MSC cocultures (n = at least 5 independent experiments for each time point, each experiment was performed in triplicate; **P < .01, ***P < .001). (B) A similar pattern was observed for the total number of CD34+ cells (n = at least 5 independent experiments for each time point, each experiment was performed in triplicate; ***P < .001). (C) Representative FACS analysis after 2 weeks of coculture of CB CD34+ cells with MSCs or CD146+ cell cocultures. After gating on CD45+CD10−CD19− cells, CD34+33− cells were defined as CD34+Lin− cells (black box). (D) The absolute number of CD34+Lin− cells was significantly higher in CD146+ cell cocultures, compared with MSC cocultures, at any time of culture (n=at least 5 independent experiments for each time point, each experiment was performed in triplicate; **P < .01, ***P < .001). (E-F) Coculture of CB CD34+ cells with MSCs led to a significantly higher frequency of CD14+ myeloid cells after 2 weeks (E) (40.24% ± 2.723% vs 26.67% ± 2.075%. n = 10 independent experiments, each experiment was performed in triplicate; ***P < .0001) and a higher frequency of CD10+/CD19+ lymphoid progenitors or mature cells after 4 weeks of coculture (F) (5.155% ± 1.918% vs 0.9541% ± 0.2564%, n = 8 independent experiments, each experiment was performed in triplicate; *P < .05). No difference in the absolute numbers of myeloid and lymphoid cells was observed between CD146+ cell and MSC cocultures. All data are presented as mean ± SEM.