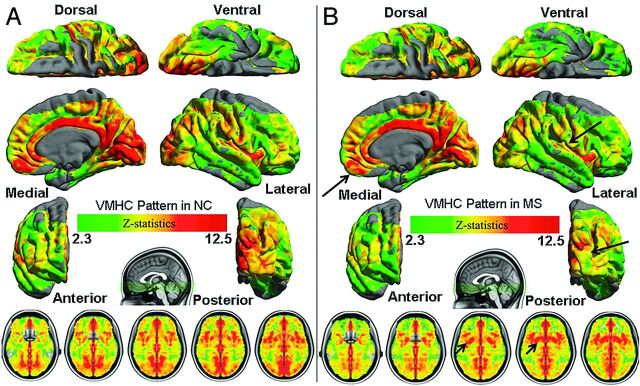
Fig 1.
Whole-brain voxelwise homotopic RSFC pattern by use of multiple linear regression models in control (A) and MS (B) groups. Homotopic RSFC was computed within 1 hemisphere (left side) for each pair of homotopic voxels and corrected by the Gaussian random field theory (minimum Z > 2.3; cluster level, P < .05, corrected). The final statistical maps are visualized as 6 hemispheric surfaces (cortical regions) with 6-mm full width at half maximum and multiple axial images (subcortical regions). Compared with control participants, patients demonstrated decreased VMHC in several cortical regions (long arrows) including the frontal, temporal, and occipital lobes and increased VMHC mainly in the subcortical regions (short arrows).