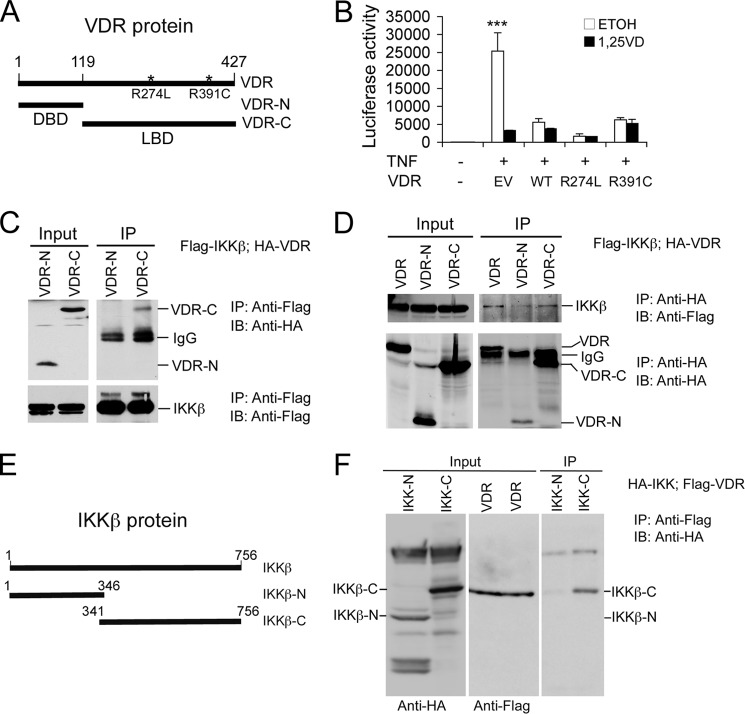
FIGURE 3.
VDR and IKKβ proteins interact through their C-terminal domains. A, schematic illustration of hVDR mutants R274L and R391C, the N-terminal portion (VDR-N) containing the DNA-binding domain (DBD), and the C-terminal portion (VDR-C) containing the LBD. B, effects of hVDR mutants on NF-κB activity. HEK293 cells were cotransfected with pNF-κB-Luc and empty vector (EV), WT hVDR, mutant hVDR(R274L), or hVDR(R391C). Luciferase activity assays were performed after TNFα stimulation in the presence of ethanol or 1,25(OH)2D3 for 24 h. ***, p < 0.001 versus the rest. C and D, HEK293 cells were cotransfected with FLAG-IKKβ and HA-VDR, HA-VDR-N, or HA-VDR-C as indicated. Cell lysates were precipitated (IP) with anti-FLAG antibodies (C) or anti-HA antibodies (D), and the precipitates were blotted (IB) with anti-HA antibodies (C) or anti-FLAG antibodies (D) as indicated. As controls, these precipitates were also blotted with the same antibodies as shown in the lower panels in C and D. Note that IKKβ interacts with VDR-C. E, schematic of IKKβ protein and its N-terminal and C-terminal constructs (IKKβ-N and IKKβ-C). F, HEK293 cells were cotransfected with FLAG-VDR and HA-IKKβ-N or HA-IKKβ-C. Cell lysates were precipitated with anti-FLAG antibodies, and the precipitates were blotted with anti-HA antibodies. The input lysates were blotted with anti-HA or anti-FLAG antibodies, respectively, as indicated at the bottom. Note that the VDR interacts with IKKβ-C and not IKKβ-N.