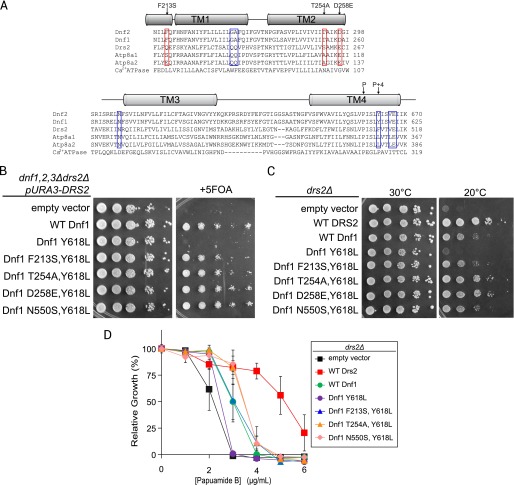
FIGURE 5.
Substitutions of specific TM1–3 residues restore function to a Dnf1 P + 4 leucine variant. A, sequence alignment of TM1–2 and TM3–4 from lyso-PC flippases (Dnf1 and Dnf2), PS flippases (Drs2, Atp8a1, Atp8a2), and Ca2+ ATPase. The blue boxes include residues reported previously as contributing to PS specificity. The red boxes indicate newly identified residues contributing to PS specificity in Dnf1 mutants that correspond to equivalent Atp8a1 residues. B, double mutants combining a p + 4 leucine (Y618L) with Atp8a1 residues (F213S, T254A, or D258E) allows Dnf1 complementation of a dnf1,2,3Δdrs2Δ strain. The 5-fluoroorotic acid kills cells that were unable to lose the URA3-marked plasmid carrying DRS2 in the parental strain. Strains that grow express a Dnf1 variant that can support the viability of dnf1,2,3Δdrs2Δ in the absence of Drs2. C, the same set of Dnf1 variants were tested for the ability to support growth of drs2Δ at 20 °C. D, similarly, each Y618L double mutant tested partially restored membrane PS asymmetry to drs2Δ relative to Y618L alone.